EDITORIAL
This issue focuses on the transition from traditional approaches to personalized, predictive, and preventive medicine, highlighting studies demonstrating the high diagnostic and prognostic value of new biomarkers (such as the sFlt-1/PlGF ratio, miRNA, and VEGF) for the early detection of preeclampsia, the risk of preterm birth, and endometriosis recurrence. Modern surgical tactics are considered, including organ-preserving hemostasis and innovative methods of perioperative analgesia that comply with enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) principles. Current data on nutritional support (omega-3 PUFAs), the prevention of thromboembolic complications, the role of micronutrients in fertility, and the impact of endocrine disruptors on reproductive health are analyzed. The review also includes case studies and historical aspects, which together form a holistic understanding of modern solutions transforming routine medical practice.
ОRIGINAL ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
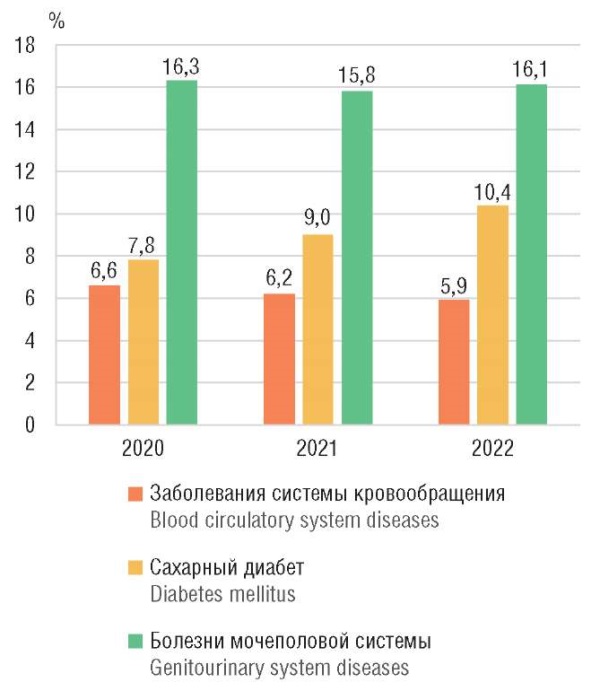
► During pregnancy, patients with extragenital pathologies are at increased risk of developing preeclampsia (РЕ).
► Placental growth factor (PlGF) and soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1) play a pivotal role in PE pathogenesis because the overproduction of either factor antagonizes the biological activity of the other, ultimately leading to developing clinical symptoms.
What are the new findings?
► The current study first ever demonstrates high diagnostic value of quantitating sFlt-1, PlGF, and sFlt-1/PlGF ratio levels for early-onset РЕ in pregnant women with pre-existing extragenital pathologies such as type 1 and type 2 diabetes, chronic hypertension, chronic pyelonephritis, and chronic glomerulonephritis.
► A cut-off value at 11.8 for sFlt-1/PlGF ratio was established, i. e., if it exceeds the threshold РЕ develops in the majority of patients with pre-existing extragenital pathologies.
► The maximum prediction window for РЕ risk onset is 6 weeks.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Introducing sFlt-1 and PIGF biomarker quantitation along with sFlt-1/PlGF ratio into routine testing practice would enable more accurate prediction of PE onset and ensure providing pregnant women timely assistance.
Introduction. Preeclampsia (PE) remains one of the most pressing issues in modern obstetrics being a leading cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. PE is a multisystem disorder that manifests after 20 weeks of gestational age, which is characterized by arterial hypertension accompanied by proteinuria and/or multiorgan dysfunction.
Aim: to quantitate the levels of biomarkers – soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1), placental growth factor (PlGF) as well as sFlt-1/PlGF ratio – in patients with pre-existing extragenital diseases for diagnostics of early- and late-onset PE.
Materials and Methods. This prospective study enrolled 439 patients with pre-existing extragenital diseases (type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic arterial hypertension, chronic pyelonephritis, chronic glomerulonephritis), divided into subgroup with PE (n = 94) and subgroup without PE (n = 345). Patients were monitored throughout pregnancy, starting from 12 weeks of gestational age. Serum PlGF and sFlt-1 levels were measured using electrochemiluminescent diagnostic tests on automated analyzers followed by calculating sFlt-1/PlGF ratio for each serum sample. In order to determine the prognostic value of sFlt1/PlGF ratio for diagnosing PE, ROC curves were created for subsequent assessing the quality of the prognosis.
Results. The timing for manifestation of early- and late-onset PE showed distinct dynamics of angiogenic biomarker changes. In early-onset PE, a statistically significant increase in sFlt-1 levels (p = 0.001) and sFlt-1/PlGF ratio (p = 0.003) was observed as early as 22–24 weeks of gestational age. In late-onset PE, the changes were less pronounced and reached statistical significance only sporadically at 25–27 weeks of gestational age (p = 0.027). While assessing PE development, alterations in the examined biomarker levels served as early predictors, preceding delivery by up to 6 weeks. For patients with pre-existing extragenital diseases, a lower cut-off value for sFlt-1/PlGF ratio was established at 11.8.
Conclusion. It may be concluded that assessing angiogenic biomarker levels provide high diagnostic value in patients with pre-existing extragenital diseases from late second to early third trimester of gestation (28–33 weeks). Examining the biomarkers' diagnostic value based on ROC-analysis revealed the following hierarchy of predictive efficacy: sFlt-1/PlGF ratio demonstrated the highest predictive value, outperforming separately quantitated either sFlt-1 or PlGF. Key metrics (sensitivity, specificity, and the area under the ROC curve – AUC) confirm that sFlt-1/PlGF ratio is the most effective predictor for diagnosing PE in the patient cohort compared with isolated measurement of sFlt-1 and PlGF magnitude. The optimal cut-off value for sFlt-1/PlGF ratio is identified at level of 11.8. It was established that the maximum predictive window for assessing risk of developing PE using this criterion is 6 weeks underscoring its high clinical value for timely identifying at-risk groups and initiating preventive measures.
What is already known about this subject?
► Endometriosis is a chronic progressive disease with a recurrent course.
► The probability of ovarian endometriosis relapse following surgical treatment remains high, reaching virtually 50 % in five-year post-surgery.
► Existing methods for relapse prediction allow to identify patients with a high risk of endometriosis relapse within the next several years, but they do not specify the timing of relapse development in a personalized manner.
What are the new findings?
► Quantitatively assessed significance of qualitative predictors for ovarian endometriosis relapse is presented that rely on the relative risk magnitude.
► The risk index (RI) was developed that takes into account the adverse impact of "n" risk factors on the body over "х" years, and allows to predict specific timing of endometriosis relapse following surgery over the next 4 years with ≥ 80 % reliability.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The presented method to predict the timing of endometriosis relapse allows synchronizing intensified preventive measures together with the period of maximum risk of disease development.
Introduction. Endometriosis affects about 10 % of reproductive age women and is characterized by a chronic relapsing course. The probability of endometriosis relapse following disease surgical treatment remains very high, which underlies a need to propose reliable, personalized approaches predicting relapse risk for choosing optimal methods to prevent relapse development.
Aim: to develop a personalized approach for assessing probability of emergence and measures to prevent ovarian endometriosis relapse following surgical intervention.
Materials and Methods. The prospective study examined 148 patients with unilateral endometrioma following surgical treatment; subsequently, the patients were divided into two groups. The main group consisted of 59 patients with endometriosis relapse, the control group included 89 patients without relapse. To create a model for predicting endometriosis relapse, there were used variables referred to categories A, B and C evidence, which increase a risk of developing post-surgery endometriosis. Treatment adherence was assessed using the AQ-25 questionnaire, the stress level – according to the Holmes-Rage method. The relative risk (RR) calculation was used while model constructing.
Results. Assessing RR magnitude, there was quantitated a significance of qualitative predictors for endometriosis relapse showing that in case smoking it was 2.4, stress – 2.0, young age (under 25 years) – 2.4, treatment adherence – 3.2, incomplete removal of endometriosis foci – 3.1, and also depended on body mass index (RR = 1.6). Relapse occurred in 18 patients during the first year post-surgery coupled to the maximum number (8.4 ± 0.5) of risk factors. During the following year, 13 new relapse cases were detected coupled to 5.3 ± 0.4 risk factors. During the third year of observation, the number of relapses increased by 12 cases, and the number of risk factors not exceeding 4.6 ± 0.2. Based on the data obtained, the risk index (RI) = n×x (conventional units) was introduced to develop a quantitative approach to assessing the specific timing of relapse development over 4 years taking into account the adverse impact of "n" risk factors on the body over "х" years.
Conclusion. In a personalized approach for assessing the risk of endometriosis relapse, the significance of evidence-based medicine qualitative predictors requires quantitative clarification. The proposed RI allows predicting specific relapse timing with > 80 % reliability. The proposed method allows synchronizing intensified preventive measures together with the period of maximum risk of disease development.
What is already known about this subject?
► The incidence of obstetric bleeding increases upon operative delivery by ≥ 5-fold. Methods for surgical hemostasis include ligation of 3 pairs of uterine vessels, application of compression sutures alone and in combination.
► Short-term sequelae include subinvolution of the uterus, endometritis, adhesions and necrosis of the uterus. Long-term sequelae may be presented as development of intrauterine adhesions and amenorrhea.
► The incidence of uterine artery recanalization after bilateral ligation does not exceed 40 %. Upon internal iliac artery ligation, a decline in ovarian reserve potential was noted.
What are the new findings?
► In patients after pathological blood loss upon cesarean section and ligation of three pairs of uterine vessels, a change in blood supply in the uterine arteries and intraovarian blood flow is observed. A reduced diameter of the uterine arteries in this group was noted that decreased down to 2.18 ± 0.02 mm and 2.09 ± 0.03 mm, averaged by 10.3 %.
► The study examines an impact of organ-preserving surgeries on female reproductive system in the future. Calculation of volumetric blood flow in the uterine arteries and the uterine arterial perfusion index (API) showed a reduced uterine vascularization. The volumetric blood flow in the uterine arteries in main vs. control group was lower in the right uterine artery by 18.2 %, in the left uterine artery – by 22.6 %. Uterine API in main group was 0.90 ± 0.02 s–1, which is significantly lower (p < 0.001) than in control group (1.29 ± 0.02 s–1).
► Highly resistant blood flow was detected in the uterine arteries and intraovarian blood flow. The pulsation index in the right uterine artery was increased to 3.67 ± 0.04, in the left uterine artery – to 3.84 ± 0.04, the resistance index values were higher than in control group and amounted to 0.92 ± 0.01 and 0.90 ± 0.02 on the right and on the left side, respectively.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► In the future, this category of patients may develop abnormal uterine bleeding presented as menstrual disorders ranging from oligomenorrhea to amenorrhea.
► Highly resistant blood flow in the intraovarian arteries can lead to developing hypergonadotropic ovarian insufficiency associated with downregulated production of ovarian steroid hormones, which in turn may lead to a compensatory increase in gonadotropic hormones – follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone.
► With timely detected highly resistant blood flow in the uterine arteries and intraovarian blood flow, it is possible to correct anovulation and luteal phase insufficiency. These interventions may result in gestation.
Introduction. To stop obstetric bleeding, organ-preserving surgical methods are used, one of which is ligation of three-layered uterine vessels. The effectiveness of organ-preserving methods comprises up to 94 %. The function of any organ depends on proper blood supply, and therefore the state of the reproductive function in women undergone organ-preserving operations is an object for further investigation.
Aim: study of blood flow in the uterus and ovaries after ligation of three pairs of uterine vessels in women with pathological blood loss.
Materials and Methods. A prospective controlled study was conducted that included main group (41 patients after ligation of three pairs of uterine vessels due to pathological blood loss during operative delivery) and control group (25 women after cesarean section without pathological blood loss and ligation of three pairs of uterine vessels). Doppler study of uterine arteries and central ovarian blood flow was performed by assessing angle-independent parameters – pulsation index (PI), resistance index (RI). Volumetric blood flow in uterine arteries and uterine arterial perfusion index were calculated.
Results. The average age of patients in main and control group was 30.00 ± 0.84 years and 25.96 ± 0.99 years (p = 0.003), respectively. The volume of blood loss in main vs. control group was 2.7 times greater (p < 0.001). Assessing PI and RI in the uterine arteries showed highly resistant blood flow, PI and RI significantly increased by 1.6 and by 1.4 times, respectively, compared with control group (p < 0.001).Calculation of volumetric blood flow in the uterine arteries in patients from main group showed a decline by 18.2–22.6 % compared to control group. It resulted in decreased arterial perfusion index of the uterus in group of patients underwent organ-preserving operations for pathological blood loss by 30.2 %. PI and IR magnitude in intraovarian blood flow turned out to increase by 2 and 1.4 times, respectively (p < 0.05).
Conclusion. The identified highly resistant blood flow in the uterus and ovaries may further result in anovulatory cycle formation due to impaired organ hemodynamics able to lead to developing ovarian insufficiency.
What is already known about this subject?
► Long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω3-PUFA) are absolutely essential for normally functioning reproduction, physiological course of pregnancy, which retard aging and tissue fibrosis in kidney and liver, myocardium, vision, brain, and skin.
► Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are the key ω3-PUFA forms crucial for physiological cessation of inflammation and for neuroprotection.
► DHA promotes the synthesis of antifibrotic metabolites protecting kidney tissue during pregnancy toxicosis and preventing development of postpartum depression. ω3-PUFA are fine tune modulation of prostaglandins (PG) biosynthesis particularly prostaglandins PGE2 and PGF2α. Excessive activity of prostaglandins PGE2 and PGF2α, stimulating neutrophil influx and cytokine production, expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (thereby enhancing its own production), negatively affects length of gestation.
What are the new findings?
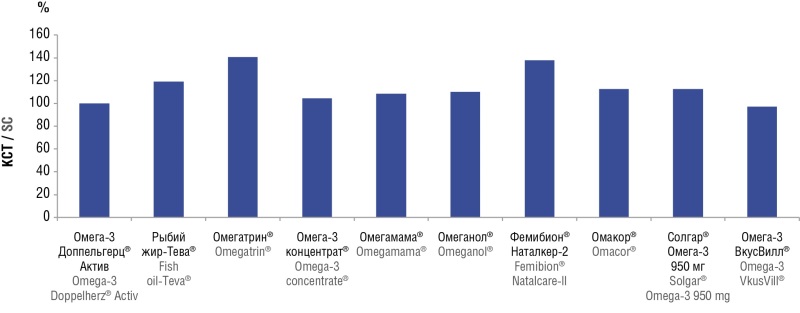
► Fatty acid composition in 10 preparations was determined for the first time by using a high-precision chromatographic assay assessing 55 chemical compounds such as 55 fatty acid metabolites.
► Total content of ω3, ω6, ω7, ω9, ω11-PUFA, EPA, DHA, EPA+DHA was determined.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Drugs with a high standardization degree for ω3-PUFA have been identified (Omacor, Femibion Natalcare-2, etc.). However, Omacor is not currently recommended for pregnant women; Omacor should be prescribed to pregnant women with caution, only after thoroughly assessed risk-benefit ratio.
► Physicians should not be subject to terminological confusion, in which all ω3-PUFA preparations are termed "fish oil": ω3-PUFAs can be manufactured without any fish oil extracts usage, e.g., extracts of marine mammal fat, algae extracts, flaxseed oil, synthetic ω3-PUFA forms.
► Drugs with a high standardization degree for ω3-PUFA have been identified (Omacor, Femibion Natalcare-II, etc.) provide support for pregnant women by contributing to normal length of pregnancy, preventing postpartum depression and improving developing fetal vision and brain, lowering risk of neonatal allergic disorders.
Introduction. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω3-PUFA) essential for female reproductive and somatic health exert a multi-faceted modulatory effect on metabolism of eicosanoids (including prostaglandins, lipoxins and leukotrienes) and docosanoids (neuroprotectins, resolvins, maresins).
Aim: to compare diverse ω3-PUFA samples assessing the degree of composition standardization for eicosapentaenoic (EPA) ω3-PUFA and docosahexaenoic (DHA) ω3-PUFA, as well as the degree of purification from fatty acid admixtures.
Materials and Methods. The work presents chromatographic analysis results for 10 ω3-PUFA-based preparations.
Results. The study allowed to reveal the compositional parameters for ω3-PUFA extracts, which can be used to distinguish between pharmaceutically standardized (Omacor, Femibion Natalcare-II, etc.) and less standardized ω3-PUFA preparations (Omeganol, Omegamama, etc.).
Conclusion. The more standardized preparation Femibion Natalcare-II is effective and safe for supporting reproductive function during pregnancy and for improving children’s neurological development. Omacor is a highly standardized preparation, however, not being officially approved for use in pregnant women.
What is already known about this subject?
► Biobanking represents an emerging biomedical field that transforms research paradigms by enabling studies through systematic biocollections. These platforms contain diverse, high-quality patient biospecimens designed for long-term storage and future research applications across multiple medical disciplines.
► Across all fields of medical science, approaches to creating research biocollections are still being developed, and their effectiveness remains to be assessed. In this article, we evaluate the feasibility of using a biocollection created by the authors according to the "longitudinal biobanking" strategy as a platform for early modeling of obstetric complication risks.
What are the new findings?
► Despite inherent complexity, "longitudinal" biospecimen collection during early gestation and predetermined monitoring timepoints enables dynamic parameter assessment throughout pregnancy. This methodology allows predictive biomarker measurement in early gestational stages, before clinical complication manifestation.
► Diverse biospecimen types within collections facilitate biomarker evaluation across biological matrices using advanced methods such as next-generation sequencing. Associated clinical data repositories enable identification of significant clinical and anamnestic predictors for obstetric complications.
► Algorithm development for early preterm birth prediction, integrating clinical, transcriptomic and proteomic data retrieved from pregnancy biobanks, demonstrates the platform's effectiveness. This validates biocollections as valuable resources for developing early warning systems for obstetric complications.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The advent of novel early prediction tools for obstetric complications may empower clinicians to implement optimal risk management strategies during pregnancy and establish effective preventive measures against severe obstetric outcomes.
Aim: to develop an algorithm for early modeling of preterm birth (PB) high risk using a biocollection of pregnancy samples created according to the "longitudinal biobanking" strategy, based on clinical, proteomic, and transcriptomic data.
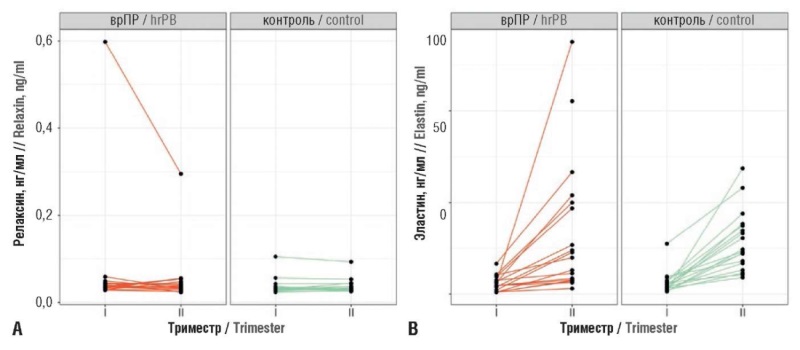
Materials and Methods. A prospective cohort study was conducted. Serum and plasma samples were retrieved dynamically from a biocollection during the first and second trimesters of gestation from 18 pregnant women with PB high risk developed cervical insufficiency (CI), and from 18 pregnant women with PB low risk not complicated by СI at any stage of gestation. Clinical and anamnestic predictors were analyzed, and serum relaxin and elastin levels, as well as marker microRNAs (hsa-miR-432-5p, hsa-miR-134-5p, hsa-miR-431-5p, hsa-miR-122-5, and hsa-miR-34a-5p) were quantitated.
Results. Based on the most significant clinical and anamnestic predictors, a proteomic predictor (serum relaxin level), and transcriptomic predictors (marker microRNAs expression) using a support vector machine (SVM), a predictive model was developed, which high efficiency was confirmed by ROC curves (AUC = 0.83 during training and 0.67 in cross-validation). This allows the developed classifier to be used as a tool for assessing PB risk.
Conclusion. Biocollections of pregnant women's samples, formed according to the "longitudinal biobanking" strategy, can serve as an effective platform for developing technologies for early predicted PB risk of obstetric complications.
What is already known about this subject?
► Elevated thrombosis may result from extremely diverse causes.
► The onset of pregnancy significantly increases the likelihood of developing venous thromboembolic events (VTE), especially in women with hereditary or acquired diseases including thrombophilic conditions.
► Disease awareness and timely risk factors assessment are important for reducing VTE risk in pregnant women.
What are the new findings?
► The «BEREG» registry provides a real-world clinical practice data on VTE assessing in pregnant women.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Proper VTE risk assessment and timely initiation of thromboprophylaxis ensure reliable prophylaxis of complications during pregnancy and postpartum period.
► Practical conclusions provided by the «BEREG» registry allow better application of the current clinical guidelines "Venous complications during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Obstetric thromboembolism".
Introduction. Recently, along with increasing women age who become pregnant and number of patients with extragenital pathology, a greater role has been referred to preconception preparation and implementation of preventive measures aimed at minimizing development of severe and often fatal conditions, particularly venous thromboembolic events (VTE), which are one of the lead cause of maternal and perinatal mortality in developed countries.
Aim: to analyze the effectiveness and safety of thromboprophylaxis in pregnant women with high VTE risk in real-world clinical practice.
Materials and Methods. The analysis was based on data obtained in the observational (cohort) study "Assessment of the clinical condition of pregnant women during gestation and childbirth in the early postpartum period and 12 months after childbirth, as well as analysis of perinatal outcomes, the condition of the fetus, newborn, and the quality of treatment for these patients" – the "BEREG" register. Inclusion criteria: pregnancy diagnosis at the first visit, the patient's written informed consent and their permanent residence in Tula or the Tula Region. Non-inclusion criteria: the patient's refusal to sign informed consent and their residence in other regions. All patient data were retrieved from outpatient and inpatient records and included complaints, medical history, information about previous and current illnesses, VTE risk factors, anthropometric data such as height, body weight, and body mass index at the time of pregnancy, as well as the type and dose of antithrombotic medication. Special attention was paid to the obstetric history, including the course of previous and current pregnancies, perinatal outcomes and delivery methods. VTE and thromboprophylaxis tactics were assessed using the "Antenatal and Postnatal Assessment of Risk Factors and Pregnancy Management" scale. The newborn's condition was evaluated by assessing birth height, weight and the Apgar score at 1 and 5 minutes of life.
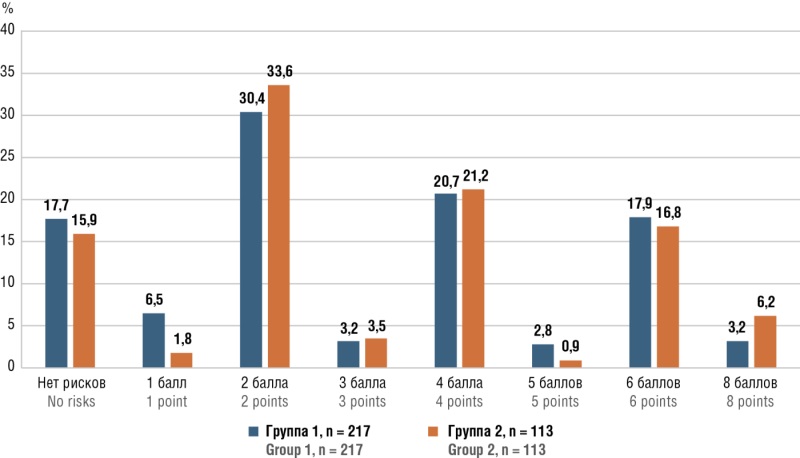
Results. A total of 3214 pregnant women aged from 15 to 46 years were included in the registry, of which 330 (10.3 %) women who received antithrombotic therapy with anticoagulants and/or antiplatelet agents, including 217 (65.8 %) pregnant women receiving combination therapy calcium nadroparin (Fraxiparin) 0.3 ml (2850 IU anti-Xa) subcutaneously per day combined with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) 150 mg/day per os (group 1) and 113 woman (34.2 %) – monotherapy with ASA 150 mg/day once per os (group 2). The groups were comparable in major clinical and laboratory characteristics. Patient management analysis showed that no cases of VTE, maternal mortality, allergic side effects, thrombocytopenia or heparin-induced thrombosis were observed in either group. However, only in the group of patients receiving ASA monotherapy there were recorded complications such as bleeding during childbirth (n = 1) and fetal death (n = 3), however, not allowing to establish a clear link with the medicine intake due to the small number of observations. It is noteworthy that doctors were not sufficiently informed about the need to use VTE risk assessment scales to optimize the management strategy, as evidenced by the lack of instructions on their use in medical records.
Conclusion. The registry showed the effectiveness and safety of thromboprophylaxis based on the 0,3 ml Fraxiparin in high-risk pregnant women in real-world clinical practice, which is confirmed by the lack of VTE, bleeding, maternal death, allergic side effects, thrombocytopenia and heparin-induced thrombosis. Of note, due to insufficient doctors' alertness about a need to apply VTE risk assessment scale for objectifying treatment strategy, the prophylactic options were chosen arbitrarily: combined therapy with low molecular weight heparin and ASA, or ASA monotherapy.
What is already known about this subject?
► Postoperative pain remains a significant clinical challenge even following minimally invasive surgery. Laparoscopic myomectomy is often associated with severe pain due to its visceral component.
► Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocol for laparoscopic myomectomy recommends multimodal analgesia, with preemptively used local anesthetics as an essential component.
► Superior hypogastric plexus block has proven effective in managing chronic pelvic pain, making it a promising technique in gynecologic surgery.
What are the new findings?
► A novel method relying on combined preemptive analgesia for laparoscopic myomectomy was developed and implemented based on laparoscopic superior hypogastric plexus block along with local anesthetic subcutaneous troacar site infiltration.
► This approach was shown to reduce opioid requirements and accelerate patient mobilization during early postoperative recovery.
► The study corroborated that postoperative pain following laparoscopic myomectomy is primarily accounted for by visceral component as evidenced by the predominance of deep pelvic pain in patients without hypogastric plexus block.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The combined preemptive analgesia technique alleviates early postoperative pain, lowers opioid requirements, and increases the safety of pain management.
► Local analgesia techniques facilitate early mobilization and shorten hospital stay that aligns with the ERAS principles.
► Routine use of laparoscopic hypogastric plexus block may improve patient quality of life and satisfaction with surgical outcomes.
Aim: to assess an impact of laparoscopic superior hypogastric plexus (SHP) block combined with preemptive troacar site infiltration on postoperative pain intensity following laparoscopic myomectomy.
Materials and Methods. The prospective randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial enrolled 207 patients undergoing laparoscopic myomectomy. Patients randomized into 3 groups with a target ratio of 1:1:1 were included in the study gradually, some (n = 9) were excluded from the study intraoperatively. Thus, the study included 198 patients: group 1 (n = 66) received standard systemic analgesia combined with troacar site infiltration and laparoscopic SHP block; group 2 (n = 65) received troacar site infiltration without SHP block; control group (group 3, n = 67) received standard systemic analgesia alone. The primary endpoint was presented by assessing pain intensity using the numeric rating scale (NRS) at 4 hours postoperatively. Secondary endpoints included NRS dynamics at 2, 6, 8, 12, and 24 hours postoperatively, time to first mobilization, opioid use, and pain quality assessment.
Results. Pain scores were significantly lower in the combined analgesia group (group 1) at all time points assessed up to 12 hours postoperatively and at discharge (p < 0.05). Opioid use in group 1 was also markedly reduced (4.5 %) compared to control group 3 (32.8 %; p = 0.001). Time to first mobilization was significantly shorter in group 1 compared to group 2 and group 3 (median 5 hours vs. 7 hours; p = 0.017). Deep pelvic (visceral) pain was more commonly reported in group 2 and group 3 than in group 1 (p = 0.021).
Conclusion. Preemptive multimodal analgesia combining troacar site infiltration with laparoscopic SHP block provides effective postoperative pain control, reduces opioid intake, and accelerates postoperative mobilization following laparoscopic myomectomy. This approach offers a promising strategy for improving recovery and minimizing opioid use in fertility-preserving gynecologic surgery.
What is already known about this subject?
► Angiogenesis, or de novo blood vessel formation, is a natural phenomenon that occurs under both normal and pathological conditions. For example, wound healing or endometrial restoration after menstruation and preparation of the endometrium for implantation involve profound angiogenic changes. Angiogenesis is also closely associated with tumor cell growth.
► The effects of angiogenesis in the human body result from a balance between angiogenic stimulators (angiogenic factors) and angiogenic inhibitors (antiangiogenic factors).
► Members of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family are major regulators of physiological and pathological vasculogenesis, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.
What are the new findings?
► For the first time, a study was conducted to assess blood VEGF level in patients with vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) and hormone-dependent malignant tumors of the female reproductive system (endometrial cancer, cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, breast cancer).
► For the first time, blood VEGF concentration in women with VVA and hormone-dependent benign tumors of the female reproductive system was determined.
► For the first time, a comparative analysis of plasma VEGF levels in women with VVA with malignant neoplasms and benign diseases of the female genital organs with healthy women (control group) was conducted.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Proper regulation of angiogenesis and vascular permeability is essential for the physiological functioning of the female reproductive tract, and many pathological conditions such as abnormal uterine bleeding, endometriosis, VVA are associated with the vascular component.
► Increased VEGF expression in women with VVA compared to healthy women may be associated with impaired vascularization and tissue regeneration in the vagina and vulva, which are further exacerbated by malignant processes
► The obtained results indicate a crucial role for VEGF in angiogenesis processes associated with malignant diseases.
Introduction. Angiogenesis is essential for growth and development of blood vessels in normal tissues, during wound healing, and a crucial factor in tumor progression. One of the main stimulators of angiogenesis is vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) that promotes active endothelial cell proliferation and migration. In malignant tumors, VEGF supports the development of tumor vessels, which may correlate with cancer prognosis and diagnosis.
Aim: to assess blood VEGF level in patients with vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) and hormone-dependent malignant tumors of the female reproductive system (breast, cervical, ovarian, and endometrial cancers), in women with VVA and hormone-dependent benign tumors of the female reproductive system and healthy women.
Materials and Methods. A cross-sectional study assessed 68 diagnosed cases of VVA and cancer of the female reproductive organs (group 1) – with breast cancer (BC), cervical cancer (CC), endometrial cancer (EC), ovarian cancer (OC); 53 women with VVA and benign diseases of the female genital organs (group 2) and 80 healthy perimenopausal women without gynecological pathology (control group). Adenocarcinoma, stage 1A was verified as a histopathological type of malignant neoplasms. Plasma VEGF concentrations were quantitated using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Blood samples were obtained by puncturing a peripheral vein before surgery. Statistical data processing was performed using the StatTech v. 4.8.5 program (StatTech LLC, Russia).
Results. The median plasma VEGF level in 80 healthy women (control group) comprised 190 (range 40.00–661.50) pg/ml, in group 1 – 452.0 (range 69.98–2808.44) pg/ml and in group 2 – 323.0 (range 95.7–1100.0) pg/ml. The median VEGF level and interquartile range in 30 patients with BBA and ВС, 10 patients with BBA and CC, 10 patients with BBA and EС, and 9 patients with BBA and ОС was 632.0 [360.0–1110.5] pg/ml, 228.0 [209.5–238.5] pg/ml, 448.0 [422.0–499.5] pg/ml and 503.0 [211.0–1337.0] pg/ml, respectively. VEGF concentrations in patients with VVA and BC, OC and EC were significantly higher than in healthy women (Mann-Whitney U-test, p = 0.001, p = 0.021 and p < 0.0001, respectively). However, in patients with BBA and CC, VEGF levels did not significantly differ from those in healthy women. The median plasma VEGF level in patients with BBA and benign diseases of the female genital organs vs. control group was significantly elevated reaching 323.0 (range 95.7–1100.0) pg/ml, which demonstrates statistically significant differences compared with the control group (p = 0.007).
Conclusion. Significant differences were found between VEGF level in women with BBA and malignant neoplasms of the reproductive system and in women with BBA and benign neoplasms of the female genital organs compared with control group (healthy women). The obtained results indicate a crucial role for VEGF in angiogenesis processes associated with malignant diseases. Increased VEGF expression in women with VVA compared to healthy women may be related to impaired vascularization and tissue regeneration in the vagina and vulva further exacerbated by malignant processes.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
► Infertility is a global health problem, with male reproductive health accounting for half of all cases.
► Antioxidant micronutrients improve sperm quality.
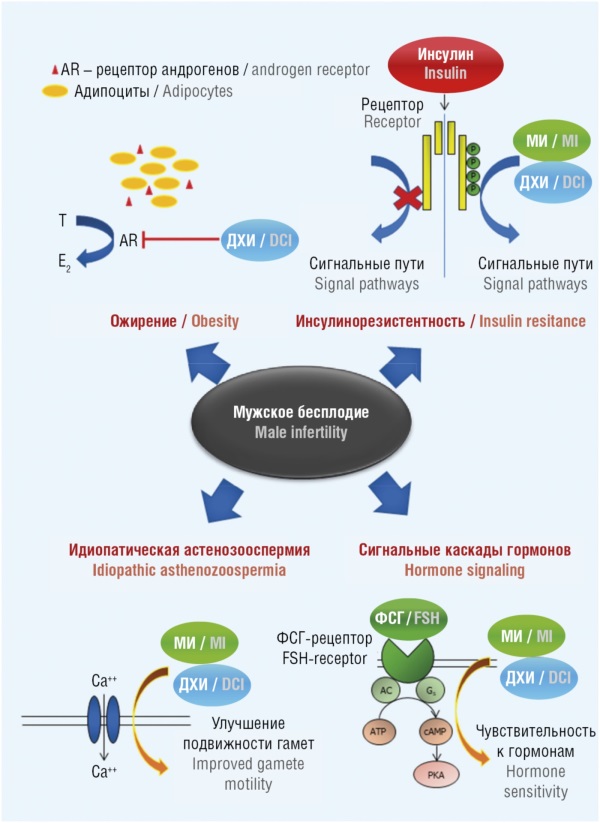
► Myoinositol (MI) and D-chiroinositol (DCI) are the building blocks for the biosynthesis of phosphatidylinositol phosphates, an essential type of signaling molecule that plays a crucial role in oocyte proliferation, morphogenesis, and growth.
What are the new findings?
► MI/DСI, their biologically active derivatives, manganese, and folate play key roles in sperm function, spanning from sperm maturation to oocyte fertilization.
► MI and DСI are essential for oocyte fertilization; manganese ions are important for gamete function acting on testosterone levels, increased antioxidant enzyme activity, and mitochondrial potential; folates, by reducing gametotoxic homocysteine levels, thereby promoting maintaining sperm DNA integrity.
► Results from experimental and clinical studies of assessing severe inositol deficiency models suggest that MI/DСI and their synergists affect sperm motility, also acting via electric fields modulation.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► It is promising to use MI/DСI in combination with organic manganese salts and folates in patients with idiopathic pathospermia, insulin resistance, obesity and oxidative stress.
An important factor of secondary male infertility is deficiency of vitamins and microelements. In the present work, a set of studies on myoinositol (MI), D-chiroinositol (DCI), their synergists (folates, manganese ions) in maintaining gametocyte structure and functioning has been systematized. MI and DCI improve the overall and progressive sperm motility by participating in signaling cascades downstream of reproductive hormone receptors (which normalizes androgen metabolism and helps prevent insulin resistance) and improving mitochondrial function. MI and DCI affect sperm maturation/functioning, motility and oocyte fertilization including those mediating inositol-dependent signaling protein phospholipase C-zeta (PLCz) and by modulating the electric fields of gametocytes. Clinical data on MI and DCI use in male infertility suggest an improved state of the zona pellucida, plasma membrane, cytoplasm and sperm reception. Manganese ions contribute to better gametocyte functioning by acting on testosterone concentration, increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes and mitochondrial potential. Folates lowering gametotoxic homocysteine levels promote maintaining sperm DNA integrity. It is promising to prescribe MI/DCI in combination with organic manganese salts and folates to patients with idiopathic pathospermia, especially paralleled with carbohydrate metabolism disorders (insulin resistance) and reduced antioxidant protection.
What is already known about this subject?
► Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDC) represent a broad class of xenobiotics capable of interfering with hormonal regulation and exerting detrimental effects on women’s reproductive health.
► It has been previously established that EDC, including bisphenol A, phthalates, and dioxins, can induce oxidative stress, disrupt hormonal balance, and accelerate ovarian reserve depletion.
► Several studies have demonstrated the ability of EDC to trigger epigenetic modifications that may be transmitted to subsequent generations, thereby amplifying their transgenerational impact.
What are the new findings?
► EDC induce apoptosis of granulosa cells, disrupt mitochondrial function, and provoke epigenetic alterations, leading to ova-
rian reserve depletion and premature ovarian insufficiency.
► Exposure to EDC alters the expression of microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs, affecting the regulation of folliculogenesis, ovulatory processes, and hormonal balance.
► Somenatural compounds and antioxidants mitigate EDC toxic effects by reducing oxidative stress, restoring intracellular signaling, and normalizing the expression of key genes in ova-
rian cells.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The use of antioxidants, signaling pathway modulators, and epigenetic regulators may be integrated into therapeutic protocols to reduce reproductive toxicity in EDC-exposed women.
► Recognizing the role of EDC in the pathogenesis of ovarian dysfunction may reshape clinical approaches to managing patients with idiopathic infertility, polycystic ovary syndrome, and premature ovarian insufficiency.
Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDC) represent a broad class of exogenous substances capable of interfering with the normal functioning of the hormonal system and exerting profound effects on female reproductive health. One of the most vulnerable targets for EDC action are ovaries, where they initiate a cascade of pathophysiological processes. This review systematizes current data on the key mechanisms of EDC-induced ovarian toxicity, including hormonal dysregulation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, epigenetic modifications, and disruption of intercellular signaling. It has been demonstrated that chronic exposure to the agents such as bisphenol A, phthalates, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and dioxins leads to impaired folliculogenesis, ovarian reserve depletion, and premature ovarian insufficiency. Furthermore, we also discuss epigenetic inheritance mechanisms through which EDC may exert long-term effects on reproductive function across generations. Special attention is paid to therapeutic strategies aimed at mitigating EDC-induced damage, including the use of antioxidants, signaling pathway modulators, and epigenetic regulators. Case studies are presented, which illustrate the global scale of environmental EDC contamination and their bioaccumulation in biological systems. The collective evidence underscors an urgent need for a multidisciplinary approach to risk assessment as well as development of preventive and therapeutic interventions to alleviate EDC impact on women’s reproductive health and to safeguard the reproductive potential of future generations.
What is already known about this subject?
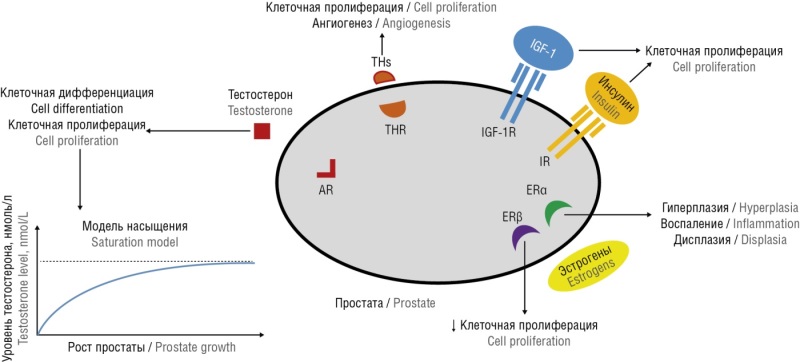
► No full understanding regarding the pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer (РС) has been achieved.
► Both BPH and PC undergo progression, and the drugs used to counter them are quite effective, but they contribute to the development of side effects that worsen the quality of life such as sexual function potentially leading to its complete cessation.
► BPH and РС exert a pronounced age-related relationship, developing extremely rarely in young and middle age men, with incidence rapidly increasing in older males by emerging in the vast majority of cases.
What are the new findings?
► This article highlights the influence of progesterone on the mechanism of developing prostate diseases and demonstrates the importance of a systemic approach not only to physiology and pathophysiology, but also to prevention and treatment.
► Natural and synthetic analogues of hormones exhibit profoundly distinct effects, which should be taken into account while using relevant drugs in practical medicine.
► The results of estrogens-related effect on the enzyme 5α-reductase are also presented, which also emphasizes the multifactorial nature of the development of complex diseases such as BPH and РС.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Attracting the attention of researchers and clinicians, it is possible to initiate clinical trials able to provide an opportunity to answer the question of whether progesterone is effective and safe to be used in clinical practice for BPH and РС prevention and treatment.
► It is also important to evaluate whether progesterone maybe more effective than 5α-reductase inhibitors currently used widely.
► Is it possible to avoid side effects such as erectile dysfunction and decreased libido that occur upon using 5α-reductase inhibitors.
The prevalence of prostate diseases primarily benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer (PC) has been progressively increasing with age being related to dramatic change in hormonal balance. Researchers and clinicians adhere to traditional understanding in developing BPH pathogenesis underlying no prominent achievements in the disease prevention and treatment. The ongoing search for gaining insights into the mechanisms behind development of these pathologies lies beyond assessing progesterone as one of the key hormones that plays an crucial role in the prostate gland functioning that has not been studied in this regard for many years. Until now, it is believed that progesterone is an exclusively "female hormone", despite that the first line therapy for BPH relies on using drugs lowering activity of enzyme 5α-reductase involved in testosterone-to-dihydrotestosterone transformation, wherein progesterone serves this function in male body under normal in vivo settings. In fact, such drugs are presented by chemical analogues of progesterone bearing minor changes in its molecule structure. In other words, to correct the pathophysiological aspects, it is necessary to proceed from the physiological basics. Presuming this, international research data available on the pathogenesis of BPH and PC as well as the effectiveness for various approaches to pathognomonic therapeutic approaches to prevent them have been analyzed.
CLINICAL CASES
What is already known about this subject?
► Genitourinary menopausal syndrome (GUMS) is associated with estrogen deficiency being accompanied not only by atrophy of vulvar and vaginal mucous membranes, but also urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and genital prolapse.
► Local estriol therapy in postmenopausal women can effectively eliminate the symptoms of vulvovaginal atrophy and urinary incontinence. The use of local estriol drugs is required while using a urogynecological pessary in menopause.
► The use of fractional CO2-laser on the vulvar skin provides visible aesthetic effect and improves the quality of vulvar skin in menopause. However, laser exposure in this area is painful, so local anesthetic such as EMLA cream may be applied.
What are the new findings?
► The article provides practical algorithms for combining methods to treat GUMS to eliminate not only atrophic changes, but also to relieve symptoms of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and genital prolapse.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The article opens up new avenues for combined or comprehensive treatment of various GUMS-related manifestations by using current evidence-based data.
Genitourinary menopausal syndrome (GUMS) manifests through a variety of clinical symptoms, such as dyspareunia, dryness of the vaginal and vulvar mucosa, and may also be associated with urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse. These conditions significantly affect the quality of life for women during menopause, contributing to their social isolation and psycho-emotional disorders. Modern approaches to GUMS treatment include the use of local hormonal drugs (mainly estriol at standard dose of 0.5 mg), such as, e.g., the original drug Ovestin in combination with surgical interventions, minimally invasive lasers, and urogynecological pessaries. Local anesthetic EMLA (lidocaine and prilocaine fix dose combination) as a safe medicine can be used prior to invasive procedures. Here, we examine clinical cases illustrating different treatment approaches for patients with various GUMS manifestations, including pelvic organ prolapse and stress urinary incontinence. In the first case, a sling urethropexy was performed with preceding estriol-based therapy that allowed to prevent postoperative complications and improve rehabilitation. In the second case, a combination of local and systemic hormonal therapy, along with a selective β3-agonist, led to markedly improved condition in a patient with overactive bladder, reducing the frequency of urination urges. A separate discussion focuses on a patient with dyspareunia, for whom fractional photothermolysis in conjunction with local hormonal therapy resulted in significant improvement in the condition of the vaginal mucosa and alleviated pain syndrome during sexual intercourse. Thus, it is necessary to follow an individualized approach to GUMS treatment by highlighting the importance of a multidisciplinary strategy that combines surgical and medical therapies with physical rehabilitation. Local hormonal therapy, the use of fractional CO2-lasers, and other methods can substantially enhance the quality of life for postmenopausal women, and the importance of these issues in clinical practice warrants further discussion and research. Providing patients with clear information about available treatment options empowers them to actively engage in managing own health, ultimately contributing to an improved quality of life.
What is already known about this subject?
► Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) has the unique ability to integrate into the human chromosomal apparatus and can be transmitted by inheritance, including vertical transmission, thereby distinguishing it from other herpesviruses and under scoring its potential relevance in perinatal medicine.
► In early childhood, HHV-6 commonly presents with roseola infantum, febrile seizures, and a mononucleosis-like syndrome; however, such manifestations typically occur after six months of age being rarely observed in neonates.
► Congenital HHV-6 infection is poorly described in the literature, which hinders clinical awareness and delays timely diagnostics in neonatal period.
What are the new findings?
► A documented case of congenital HHV-6 infection in a full-term newborn is first presented in Russian clinical practice, diagnostically verified by positive PCR data in both blood and saliva samples within the first days of life.
► A systematic analysis of clinical, laboratory, and instrumental data was conducted, enabling a comparison of the presented individual case with current knowledge on herpesvirus infections in neonates and contributing to broader understanding of their neonatal clinical forms.
► The diagnostic value of simultaneously examined both the newborn and paired mother including molecular methods applied within the first hours of neonatal life has been emphasized for detecting potential HHV-6perinatal transmission.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Routine inclusion of HHV-6 in the diagnostic panel for neonates presenting with unexplained fever may facilitate earlier diagnostics, reduce unnecessary empirical antibiotic therapy, and improve overall quality of neonatal care in early postnatal period.
► A new clinical awareness has been emerging among neonatologists and infectious disease specialists regarding a potential for vertical transmission of herpesviruses not routinely included in the TORCH group. This may lead to a revised current diagnostic approaches for neonatal exanimation.
► The scope of PCR diagnostics has been expanding in routine neonatal practice in cases of suspected intrauterine infection of unclear etiology additionally assessing saliva and umbilical cord blood samples for early diagnostic verification.
Neonatal human herpesvirus type 6 (HHV-6) infection is an extremely rare disease. HHV-6 is a unique virus because it is able to integrate into human chromosomes to be further transmitted vertically from parent to offspring. In humans, HHV-6 is associated with a wide range of clinical manifestations and, in children, may present as roseola infantum, febrile seizures, aphthous stomatitis, mononucleosis-like syndrome, or fever of unknown origin. This article reports a rare case of congenital HHV-6 infection in a newborn. To date, both Russian and international publications provide very limited descriptions of such cases, which, in our opinion, reflects a significant knowledge gap among neonatologists regarding this condition. We discuss the clinical forms of HHV-6 infection in neonates, rare case presentations, and current approaches to diagnosis and treatment.
FROM HISTORY
During physiological (normal) childbirth, the third (placental) period of labor is the most crucial for the mother. The placenta becomes separated by natural forces (uterine contractions) and the placenta is released (born) by the mother's efforts. If the latter is ineffective, the placenta is removed from the uterus artificially, using special methods. The duration of the placental period is determined within 15–30 minutes. During this period of time, signs of placental separation are carefully monitored and, if they appear, the placenta is removed from the birth canal. Among the well-known relevant signs, one is named after the authors – the Küstner–Chukalov’s sign. While delivering student classes, attention was drawn to the different spellings of this sign both in obstetrics textbooks and in special publications. This article studies primary sources in order to unify the name of the "Küstner–Chukalov’s" sign of placental separation.
EVENTS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2500-3194 (Online)