EDITORIAL
This issue focuses on the translation of molecular and clinical-instrumental indicators into personalized solutions in obstetrics and gynaecology. In gynaecological oncology, the discussion covers integrated biomarkers of thrombotic risk (vWF/ADAMTS-13 axis, antiphospholipid antibodies) and the potential for organ-preserving interventions, including robot-assisted procedures. In reproductive medicine, the issues addressed include preconception care of deficiencies (e. g. iron and folate), assessment of the uterine cavity in older patients and predictors of adverse perinatal outcomes in cases of premature rupture of membranes. Reviews on the Wnt/β-catenin cascade in endometriosis, molecular genetic markers of breast cancer, and nanotechnology provide a foundation for developing diagnostic panels and targeted approaches. A clinical case study of vaginal reconstruction and a historical essay complement the practical and educational content of the issue.
ОRIGINAL ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
► In cancer patients, elevated von Willebrand factor (vWF) level and reduced metalloprotease ADAMTS-13 activity are indicative of endothelial dysfunction as well as increased thrombotic potential, which is associated with elevated risk of venous thromboembolic events (VTE).
► A deficiency in ADAMTS-13 activity results in accumulation of ultra-long vWF multimers potentiating thrombogenesis and predisposing to microangiopathy.
► In gynecologic oncology patients, chemotherapy worsens the vWF/ADAMTS-13 imbalance, thereby enhancing hypercoagulable state and endothelial injury.
What are the new findings?
► High prognostic significance of the vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio in gynecologic oncology patients was demonstrated for early stratification of risk for chemotherapy-related VTE.
► The optimal threshold for the vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio was determined to be ≥ 1,6, providing the best balance between sensitivity and specificity for predicting high VTE risk.
► The effectiveness of anticoagulant prophylaxis and therapy correction can be assessed using dynamic vWF/ADAMTS-13 monitoring.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Introducing vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio monitoring in VTE risk stratification algorithms for gynecologic oncology patients would enable the individualization of anticoagulant prophylaxis.
► Using the vWF/ADAMTS-13 indicator in conjunction with traditional clinical risk scales will increase accuracy of VTE prediction.
► Using the vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio to monitor treatment dynamics may allow to properly assess the effectiveness of anticoagulant prophylaxis and adjust therapy protocol timely.
Aim: to evaluate a prognostic significance for the vWF/ADAMTS-13 (von Willebrand factor/a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13) ratio as an integral biomarker for stratifying the risk of venous thromboembolic events and for monitoring the effectiveness of prophylactic anticoagulant therapy (АСТ) in gynecologic oncology patients receiving chemotherapy.
Materials and Methods. This prospective cohort interventional comparative study included 74 patients with ovarian cancer (OC) or cervical canal adenocarcinoma who were undergoing chemotherapy. The patients were divided into groups depending on whether they had experienced thrombotic complications earlier. Levels of vWF, ADAMTS-13, and the vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio, as well as D-dimer, were assessed. Laboratory parameters were analyzed before chemotherapy, after 1–2 courses, and during prophylactic ACT. Variation statistics, ROC analysis and the Youden criterion were used to determine the threshold values.
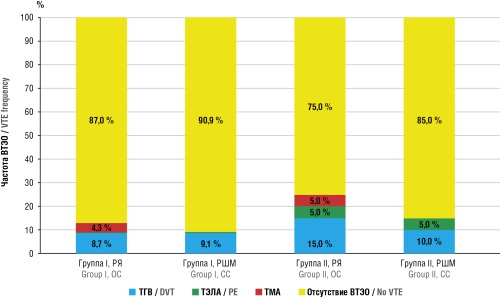
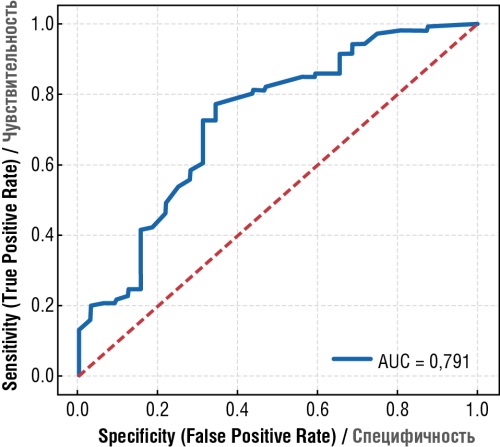
Results. Significant disturbances in vWF/ADAMTS-13 axis parameters were detected in patients with pre-chemotherapy thrombotic history, compared to control group: the ratio reached 1.59–1.65 (p < 0.05), compared to 0.65 in control group. During chemotherapy, such alterations worsened (up to 2.04 in OC patients), accompanied by elevated D-dimer level. Administering prophylactic ACT based on low molecular weight heparin normalized the vWF/ADAMTS-13 axis parameters and decreased D-dimer level, reflecting a reduced prothrombotic potential. The incidence of thrombotic complications upon anticoagulant prophylaxis was twice as low as without it (13 % vs. 25 %). ROC analysis confirmed the high diagnostic significance for the vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio (AUC = 0.87), with an optimal threshold value of ≥ 1.6 for identifying the high-risk group.
Conclusion. The vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio is a sensitive, integral marker of hypercoagulability. It allows to justify stratification of thrombotic complication risk and monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant prophylaxis in gynecologic oncology patients receiving chemotherapy. Including vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio in clinical algorithms can improve the accuracy to select patients for anticoagulant prophylaxis and facilitate treatment personalization.
What is already known about this subject?
► Premature rupture of membranes (PROM) accounts for approximately 30 % of all preterm births. The use of antibiotics and corticosteroids can prolong the latency period and improve perinatal outcomes.
► PROM is often combined with the development of manifest chorioamnionitis and systemic inflammatory reaction syndrome in the fetus by worsening neonatal outcomes.
► PROM poses a significant challenge in obstetrics, especially at early gestational ages. Early detection, close monitoring, and timely intervention can improve outcomes for both the mother and the neonate.
What are the new findings?
► Unfavorable perinatal outcomes were statistically significantly more often combined with higher blood C-reactive protein (CRP) level and leukocyte count in pregnant women with PROM before childbirth, as well as the amniotic fluid index (AFI) before delivery < 32.0 mm.
► The presence of widespread ecchymosis in premature infants at birth can be considered as a negative prognosis predictor.
► Ureaplasma parvum was detected significantly more often in newborns with poor outcomes.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The prenatal AFI < 32.0 mm can be used in routine practice as one of the most objective risk factors for unfavorable perinatal outcomes.
► Our study confirmed the presence of chorioamnionitis without maternal fever, suggesting that greater attention should be paid to subclinical forms of intra-amniotic infection.
► Active prevention of Ureaplasma parvum will improve outcomes in premature infants.
Introduction. Approximately 10 % of patients with preterm labor exhibits signs of intra-amniotic inflammation, which often occurs subclinically and results in increased risk of premature rupture of membranes (PROM).
Aim: to identify predictors of unfavorable perinatal outcomes associated with PROM.
Materials and Мethods. The single-center retrospective cohort study was conducted from January 1 to November 1, 2023 by enrolling patients between 28 0/7 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation with PROM. A total of 176 maternal and neonatal medical records were analyzed. Two groups of neonates were identified: Group 1 – neonates with favorable outcomes at the time of hospital discharge; Group 2 – fetuses or neonates with unfavorable outcomes at discharge (including antenatal fetal death, neonatal death, grade 3 intraventricular hemorrhage, periventricular leukomalacia, severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia, or surgical-stage necrotizing enterocolitis). There were analyzed maternal medical histories, pregnancy and delivery data, amniotic fluid index (AFI), maximum vertical pocket of amniotic fluid, severity of respiratory failure and central hemodynamic disturbances in premature neonates, as well as incidence rates for those born to mothers with PROM. Multivariate analysis was conducted to identify factors associated with neonatal outcomes.
Results. Antenatal fetal death was recorded in 7 of 176 cases (3.9 %), and neonatal mortality among live-born infants comprised 7 of 169 (4.1 %). Median gestational age at delivery in Group 2 was 193.0 days [IQR: 180.0–198.0], significantly lower than in Group 1 (238.0 days [IQR: 223.5–247.0]; p < 0.001). Chorioamnionitis (p < 0.001) and anhydramnion (p = 0.003) were significantly more frequent in Group 2. Neonates in Group 2 required tracheal intubation (p < 0.001), surfactant therapy (p < 0.001), mechanical lung ventilation (p = 0.029), and high frequency oscillatory ventilation (p < 0.001) more often within the first 72 hours of life. NEOMOD (Neonatal Multiple Organ Dysfunction) scores were significantly higher in this group (p < 0.001). In Group 2, Ureaplasma parvum in nasopharyngeal swabs was more frequently found by using polymerase chain reaction (p = 0.015).
Conclusion. Predictors of adverse outcomes in fetuses and preterm neonates with PROM consisted of anhydramnios, chorioamnionitis, lower gestational age and birth weight, cesarean delivery, elevated maternal C-reactive protein (CRP) and white blood cell count prior to delivery, an AFI ≤ 32.0 mm, higher NEOMOD scores, presence of diffuse ecchymosis at birth, detection of neonatal Ureaplasma parvum, lower hemoglobin levels, as well as increased procalcitonin and CRP levels within the first 72 hours of life.
What is already known about this subject?
► Chronic endometritis (СЕ) is a common cause of implantation failure and recurrent miscarriage.
► Standard histological methods show low sensitivity in CE diagnostics.
► Immunohistochemical (IHC) diagnostics based on assessing CD138 marker expression and hysteroscopy markedly increase the accuracy for detecting endometrial inflammation.
What are the new findings?
► A high incidence of severe CE has been demonstrated in women of advanced reproductive age.
► The need for mandatory hysteroscopic and IHC assessment before applying the assisted reproductive technology (ART) program has been confirmed.
► For the first time, the data on endometrial pathology in the Kazakhstan patient cohort related to in vitro fertilization (IVF) are presented.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Prior to embryo transfer, office hysteroscopy and IHC should be included in examination algorithm for ≥ 35-year-old patients.
► Timely detection and treatment of CE may allow for lowering number of unsuccessful IVF cycles.
► A personalized approach to uterine cavity assessment may improve outcomes of ART programs.
Introduction. Successful completion of in vitro fertilization (IVF) program is characterized by pregnancy achievement, suggesting that an implantation-competent embryo has reached a receptive endometrium. Chronic endometritis (CE) often being asymptomatic or presented with non-specific symptoms represents one of the main causes for impaired endometrial receptivity. CE treatment and normalization of CD138 expression are related to improved outcomes in assisted reproductive technology (ART) programs, primarily in women of advanced reproductive age.
Aim: to analyze the frequency and severity of pathological endometrial changes by using hysteroscopy with biopsy and immunohistochemical examination (IHC) in women of advanced ( 35 years old) vs. younger (< 35 years old) reproductive age.
Materials and Methods. A retrospective descriptive continuous cross-sectional study was conducted to analyze 569 hysteroscopy protocols with biopsy and IHC performed at the "PERSONA" clinic in 2020–2022. Clinical and anamnestic data (age, frequency of primary and secondary infertility), frequency, structure and severity of uterine cavity pathology, age-related pattern were assessed according to histological and IHC studies in two age groups: < 35 years and ≥ 35 years.
Results. CE was identified in 80.47 % of younger and 85.3 % of older patients. Severe CE was significantly more common in ≥ 35-year-old women (12.73 % vs. 3.6 %; p = 0.021). No significant inter-group differences were found in CD138 expression levels. Common endometrial abnormalities included fibrosis and mixed lesions.
Conclusion. While overall endometrial pathology was commonly observed in both age groups, severe CE forms were significantly more frequent in women of advanced reproductive age. Office hysteroscopy is recommended prior to ART initiation in this population to optimize outcomes.
What is already known about this subject?
► Oncogynecological patients are at high risk of venous thromboembolic complications (VTE) when cancer per se is combined with aggressive antitumor treatment.
► Congenital thrombophilias, such as the FV Leiden and prothrombin G20210A mutations, are associated with elevated thrombosis risk.
► Circulation of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) is often found in cancer patients that contributes to VTE recurrence.
What are the new findings?
► It has been established that a high frequency of multigenic and combined thrombophilia is a predictor for recurrent VTE in oncogynaecological patients.
► The importance of altered vWF/ADAMTS-13 axis as an indicator of endothelial dysfunction in case of recurrent thrombosis is demonstrated.
► The need for comprehensively assessing congenital, acquired and inflammatory factors to stratify risk of recurrent VTE has been substantiated.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Monitoring of vWF and ADAMTS-13 can be introduced into practice to assess a risk of recurrent VTE and proper anticoagulant therapy.
► While planning VTE prevention in oncogynaecological patients, detected genetic thrombophilia and aPL, as well as related titer range should be taken into account allowing to personalize therapy duration and extent.
► COVID-19 convalescent patients may be applied with more aggressive anticoagulant prophylaxis strategies taking into account increased recurrent VTE risk.
Aim: to identify the key pathogenic factors and triggers associated with recurrent venous thromboembolic events (VTE) in gynaecological oncology patients.
Materials and Methods. There was conducted a retrospective cohort study with three groups of gynaecological oncology patients: 155 women with a history of thrombosis episodes (Group I), 66 patients with recurrent thrombosis and stage III–IV ovarian cancer (Group II), and 72 patients with tumours of the female genital organs who had previously contracted SARS-CoV-2 infection (Group III). All patients underwent comprehensive assessments for congenital thrombophilia (FV Leiden, prothrombin G20210A, MTHFR C677T, PAI-1 and platelet glycoproteins), acquired thrombophilia (anti-β2-GP1 antibodies, anti-annexin V antibodies, and anti-prothrombin antibodies), and markers of endothelial dysfunction – von Willebrand factor (vWF) and metalloprotease ADAMTS-13, and thromboinflammatory syndrome (D-dimer). Statistical analysis was performed using non-parametric tests at a significance level set at p < 0.05.
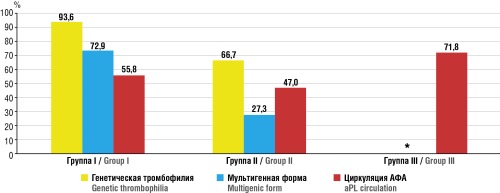
Results. Recurrent VTE in gynaecological oncology patients was found to develop upon high prevalence of congenital and acquired thrombophilia, vWF/ADAMTS-13 axis disorders, and activation of the thromboinflammatory syndrome. In group I, genetic thrombophilia was detected in 145 patients (93.6 %), with multigenic variants occurring in 113 patients (72.9 %); antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) circulation was found in 87 patients (55.8 %). In group II, genetic thrombophilia was detected in 44 (66.7 %) women and aPL circulation in 31 (47.0 %); the median vWF level was 1513 IU/L (p < 0.05); D-dimer levels exceeded 1500 ng/ml in 48 patients (72.7 %) with median 2700 ng/ml. In group III, recurrent VTE were observed in 39 (54.2 %) patients. The median vWF level was 3450 IU/L and ADAMTS-13 level was reduced down to 220 IU/L (p < 0.01) compared to group I and group II. The D-dimer level exceeded 1500 ng/ml in 33 patients (84.6 %) with median 2900 ng/ml. Circulating aPL was detected in 28 patients (71.8 %) with relapses. COVID-19 convalescent patients had 70 % higher recurrence risk (relative risk (RR) = 1.7; 95 % confidential interval (CI) = 1.1–2.8; p < 0.05).
Conclusion. Recurrent VTE in oncogynaecological patients has a multifactorial etiology, collectively accounted for by congenital and acquired thrombophilia, endothelial dysfunction, and thromboinflammatory syndrome, which may be profoundly exacerbated by previous SARS-CoV-2 infection. The data obtained emphasize a need for comprehensively assessing risk factors and applying an individualized approach to prevent VTE recurrence in this patient group.
What is already known about this subject?
► Lichen sclerosus (LS) is classified as an orphan disease. Recently, its incidence has increased among women.
► The real-life LS prevalence is not determined due to the large number of asymptomatic cases and observation of patients by different specialists, which leads to erroneous diagnoses.
► In total LS incidence of in women, 15 % falls on prepubertal age. In 2000, the data were obtained showing that LS rate in girls aged 2–16 years comprises 1:900.
What are the new findings?
► The 28-year-long dynamics in the number of LS girls aged 0 to 18 years in the Republic of Bashkortostan (RB) was studied.
► The registration of patients with verified LS diagnosis allowed to determine a real-life LS prevalence among girls in the RB.
► The relationship between the incidence and the periods of girls' childhood was examined. LS incidence among girls in cities and rural areas of the RB was compared.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Studying LS epidemiology may contribute to identify risk groups and, ultimately, improve LS diagnostics.
► Each childhood period is characterized by emerging specific diseases associated with the stages of body systems development. Studying the patient age of disease onset may us to assess underlying causes and propose methods for etiotropic therapy.
► Studying an impact of social factors such as the patient’s place of residence may help to clarify the risk factors for LS emergence and develop measures to prevent it.
Aim: to study the features of lichen sclerosus (LS) epidemiology in girls from the Republic of Bashkortostan (RB).
Materials and Methods. A retrospective cohort study was conducted. The authors analyzed LS incidence in girls aged 0 to 18 years, the data provided by two pediatric gynecological department, which in different years served all RB girls with gynecological pathology. A comparison of indicators recorded during the two equal and comparable time periods was carried out: the first 9 years of operation (from 1996 to 2004) at the Department of Pediatric Gynecology of the Clinical Hospital of Emergency Medical Care, Ufa and the first 9 years of operation (from 2015 to 2023) at the Gynecological Department of the Republican Children's Clinical Hospital, Ufa.
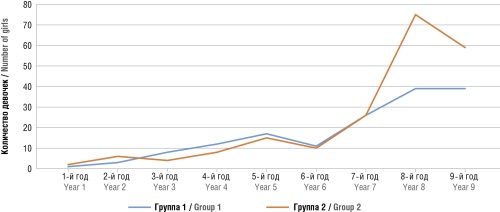
Results. Lichen sclerosus in RB girls can be attributed to orphan disease, since its incidence rate over the past 9 years comprised 0.46 ‰. Over the 19-year follow-up (2004–2023), the accumulated LS incidence in RB girls aged 0 to 18 years increased from 0.22 to 0.46 ‰, and in Ufa – from 0.35 to 0.65 ‰.
Conclusion. In recent years, a significant increase in LS incidence in girls has been observed in the RB. Most LS patients are in the prepubertal childhood period.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
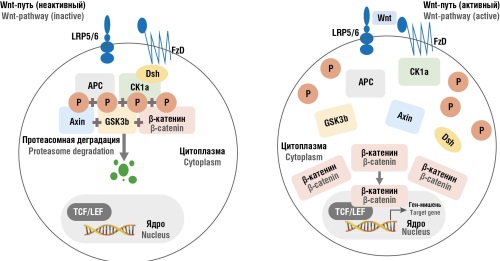
► The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway regulates cell proliferation, migration, and fibrosis.
► The Wnt/β-catenin pathway hyperactivation is observed in multiple neoplastic processes, such as endometriosis.
What are the new findings?
► MicroRNAs (miR-30c, miR-488) have been identified as modulators of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in endometriosis.
► Proteins that activate and regulate Wnt-signaling axis have been characterized.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► MicroRNAs represent promising candidate biomarkers for non-invasive endometriosis diagnostics.
► Targeted therapy against the Wnt/β-catenin pathway could enhance endometriosis treatment.
Endometriosis is a chronic estrogen-dependent disease characterized by the ectopic growth of endometrium-like tissue outside the uterus. In recent years, increasing attention has been paid to the role of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in endometriosis pathogenesis, wherein it regulates cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and fibrosis. Hyperactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin cascade promotes disease progression, chronic inflammation, and adhesion formation. MicroRNAs modulating this signaling pathway are of particular interest, offering potential for endometriosis diagnostics and targeted therapy. Further research may lead to new treatment approaches and improved quality of patients’ life.
What is already known about this subject?
► About 30 % of cervical cancer (СС) and 12 % of ovarian cancer (ОС) cases are diagnosed in women under the age of 45, thereby highlighting fertility preservation issues as clinically significant.
► Organ-preserving treatment is possible for СС stage IA–IB1, epithelial ОС stage IA-IC1 and highly differentiated stage I endometrioid cancer.
► Since 2005, robot-assisted surgery has been used in oncogynecology; with its oncological effectiveness validated to be comparable to that of laparotomy in tumors < 2 cm size.
What are the new findings?
► The incidence of pregnancy after robotic radical trachelectomy reaches up to 72 %, and live births extend more than 86 % at gestational age of ≥ 32 weeks.
► With organ-preserving treatment of endometrial cancer using hysteroscopy and progestins, complete remission is achieved in 79 % of patients, pregnancy is observed in 35–53 %.
► In women with borderline ovarian tumors, the five-year survival rate reaches 99 %, the recurrence rate after organ-preserving treatment comprises up to 30 %, pregnancy occurs in 82–85 % of cases.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The integration of robotic technologies into organ-preserving treatment can expand indications by increasing accuracy and reducing complications.
► Successful cases of robotic uterus transplantation open up an avenue for treating cancer-related absolute uterine infertility.
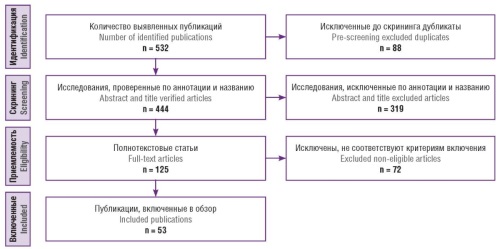
Aim: to systematize and analyze current data on the use of minimally invasive and robot-assisted interventions in the treatment of gynecologic malignant tumors in reproductive age women who wish to preserve fertility.
Materials and Methods. The search was conducted in the PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, and eLibrary databases among the primary sources published from 01.01.2000 tо 28.02.2025. There were retrieved keywords and MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) terms including: “robotic surgery”, “robot-assisted surgery”, “fertility preservation”, “gynecologic cancer”, “cervical cancer”, “endometrial cancer”, “ovarian cancer”, “reproductive age”, “minimally invasive surgery”, “uterine transplantation”, as well as the corresponding Russian terms. Original studies focusing on oncologic and reproductive outcomes in women under the age of 45 were included in the analysis. The methodology followed the PRISMA guidelines. The final analysis included 53 publications.
Results. The data evidence about the effectiveness and oncologic safety of fertility-preserving approaches in early-stage cervical, endometrial, and ovarian cancer. Robot-assisted interventions vs. conventional techniques demonstrated comparable or superior outcomes in fertility preservation with fewer complications and faster recovery. Additional topics addressed include ovarian transposition, uterine transplantation, and alternative fertility preservation strategies.
Conclusion. Robot-assisted surgery extends the potential for fertility-sparing treatment of gynecologic malignant tumors in reproductive age women. Such interventions should be performed in specialized centers by multidisciplinary teams. Further research is needed to standardize treatment protocols and evaluate long-term oncologic and reproductive outcomes.
What is already known about this subject?
► Iron deficiency remains common worldwide. Maintaining normal iron and folic acid metabolism becomes of special importance during pregnancy.
What are the new findings?
► The convenience of combined therapy with iron and folic acid was scientifically justified, additionally showing the advantage of small-dose and prolonged-release preparations. This allows to reduce the risks of side effects such as development of ferroptosis and other undesirable phenomena due to reactive oxygen species.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The use of combined iron and folic acid supplements during pregnancy planning and throughout pregnancy can reduce the incidence of iron deficiency anemia, the risk of neural tube defects in the fetus that results in decreased risks of adverse outcomes for both the mother and the fetus.
Information published over the last decade on using iron supplements has been collected and systematized. The need for long-term iron supplementation and patient compliance has been updated and emphasized. The main requirements for current iron supplements today have been formulated, and the advantages of combining organic iron salts with folic acid as the most optimal and contemporary approach to the prevention and treatment of iron deficiency during pregnancy have been emphasized.
What is already known about this subject?
► The datasets collected in The Cancer Genome Atlas reveal foundational data for identifying new biomarkers for breast cancer (BC). According to the latest data, 14 and 6 messenger RNA (mRNA) with downregulated and upregulated expression, respectively, were identified. Сurrent BC-related genetic studies focus on assessing BRCA, PALB2, ATM, CHEK2, RAD51C, RAD51, BARD1, and TP53 genes.
► The introduced triple classification of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status – HER2-low (low expression), and HER2+ positive mirrors new approaches in therapy, because precisely identified HER2 expression levels is crucial for personalized patient treatment.
► Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) are recognized as a significant prognostic factor in the early stages of triple-negative ВС (TNBC) that may become assessed as a standard parameter.
What are the new findings?
► Quantitative assessment of circulating tumor cells (CTC) relying on system CellSearch® databases shows a peak level of clinical validation being a secure data source on current metastatic lesions for cell counting and molecular characterization. The use of such systems allows for real-time monitoring, identify ingindividual biomarkers and their combinations.
► TIL, PD-L1, and Foxp3+ Treg have been confirmed as independent BC prognostic factors. Somatic mutations in PIK3CA are a predictor of response to PI3K inhibitors in metastatic breast cancer ER+ and HER2–. TIL is the first biological prognostic biomarker for early-stage TNBC. A link between high TIL level and a more favorable prognosis is established.
► Prior endocrine therapy with aromatase inhibitors, tamoxifen, and fulvestrant can lead to ESR1 mutations and therapy resistance. A fully oral combination of elacestrant and alpelisib, in conjunction with prior treatment, is clinically effective in patients with ESR1 and PIK3CA mutations.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► In the future, the simultaneous detection could potentially expand to encompass up to 100 mutations across many genes and might be used for large-scale analysis of CTC and circulating tumor DNA levels.
► Information about the characteristics of BC stem cells, main factors, and tumor microenvironment, will allow exploring new methods to impact the mechanisms of stem cell tumor transformation and develop treatment methods.
► A comprehensive analysis of TIL and PD-L1 levels may be utilized to reveal indications for therapy using PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors.
Introduction. Breast cancer (BC) is the most common oncology pathology that holds a leading place among the causes of cancer death. Early diagnosis is critically important for successful treatment. Current molecular genetic research has revolutionized oncology allowing to classify breast cancer into various subtypes and, thereby, radically changing the approach to therapy.
Aim: to analyze the literature data on up-to-date information regarding the molecular genetic BC markers and the prospects of their use for BC diagnostics and treatment.
Materials and Methods. In accordance with the PRISMA guidelines, a systematic search was conducted in the PubMed/ MEDLINE, eLibrary, and Google Scholar databases using Russian and English keywords: «breast cancer», «early breast cancer», «molecular markers of tumor cells», «chemotherapy», «hormone therapy», «estrogen and progesterone receptors», «triple-negative breast cancer», «neoadjuvant chemotherapy», «complete pathological response», «immunohistochemistry». Peer-reviewed publications in Russian or English containing original data on BC molecular diagnostics were included, with total of 39 publications selected for analysis.
Results. High diagnostic and prognostic value was found for mutations in the BRCA1/2, PIK3CA, TP53, CHEK2, PALB2, and ESR1 genes, as well as for the expression of PD-L1, TIL (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes), and Foxp3+ regulatory T cell levels. Modern technologies such as liquid biopsy, analysis of circulating tumor cells, and circulating tumor DNA allow for real-time tumor molecular profiling. This markedly expands the potential for personalized treatment strategies. HER2-low subtype and ESR1 mutations require individualized therapeutic approaches.
Conclusion. BC molecular markers have become a cornerstone for accurate diagnosis, risk stratification, and personalized therapy. Despite substantial research advances, the accessibility of molecular diagnostics, standardization of procedures, and integration of innovative technologies into clinical practice remain pressing issues. Systemic support is needed to implement molecular techniques into standard care protocols and ensure their broader application in real-world oncology settings.
What is already known about this subject?
► Nanotechnologies play an important role in medicine, impro-
ving the diagnostics and treatment of female reproductive system cancer through targeted drug delivery.
► Modern therapeutic methods (surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy) for gynecological tumors have limitations, including high toxicity and side effects.
► Nanoparticles are used to increase tumor cell-specific selectivity of effects and reduce systemic toxicity of traditional treatment methods.
What are the new findings?
► The use of liposomes, polymer and protein nanoparticles increases the effectiveness of chemotherapy, ensuring targeted effects on tumor cells with minimal impact on healthy tissues.
► The use of gold-silver nanoparticles, quantum dots and magnetic nanoparticles allows to detect oncological diseases earlier, especially cervical cancer, due to its high sensitivity to human papillomavirus (HPV) biomarkers and DNA.
► The use of nanovaccines consisting of antigens and nanoparticle-based adjuvants, enhances antitumor immune response and opens up new avenues for more effective treatment of HPV-associated tumors.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Introduction of nanotechnologies in oncology may improve the effectiveness of treatment and reduce toxic effects of standard therapeutic approaches.
► The use of nanoparticles in diagnostics will allow earlier detection of tumor processes, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
► Development of personalized medicine using nanotechnology may allow to fine-tune treatment to patients’ individual characteristics, reducing a relapse risk.
Introduction. By enhancing detection accuracy, therapeutic effectiveness and minimizing side effects, nanotechnology may contribute to improve diagnostics and treatment of patients with female reproductive system cancer.
Aim: to summarize current literature data and assess а role of nanotechnology in treatment of cervical cancer (CC), ovarian cancer (OC), endometrial cancer (EC) and reveal gaps requiring further research.
Materials and Methods. The search was carried out in the electronic databases PubMed/MEDLINE, Google Scholar and eLibrary using the following keywords: “gynecological cancer”, “targeted therapy”, “cervical cancer”, “ovarian cancer”, “endometrial cancer”, “nanotechnology”, “nanoparticles”. All works were published between 2011 and 2024.
Results. Nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems represent a promising approach to the treatment of female reproductive system oncology, providing precise drug delivery directly to tumor cells. Such systems, including liposomes, nanoparticles, micelles, and dendrimers, are characterized by advanced efficiency, reduced toxicity, as well as the opportunity for controlled release of active components. Nanotechnologies increase the effectiveness of vaccines by prolonging their half-life, affect the СС microenvironment and potentiate the antitumor immune response with minimal toxicity. Nanovaccines are capable of delivering antigens and adjuvants directly to immune cells, enhancing immune response and improving ОС treatment results. Nanotechnologies show prominent potential in improving EC treatment despite that their role in this context remains understudied compared to other types of female reproductive system cancer.
Conclusion. Nanoparticles can carry both conventional drugs as well as protein- and nucleic acid-based systems directly to cancer cells. However, only a few nanoparticle-based treatments for female reproductive system cancer have been approved for use. The field is making significant progress toward more effective and widely available treatments.
CLINICAL CASE
What is already known about this subject?
► Secondary vaginal atresia is an exceptionally rare pathology which usually results from radiation therapy or extensive surgery.
► Secondary vaginal atresia can only be treated surgically.
What are the new findings?
► Introduction and utilization of the Martius-Symmonds labial flap was described for vaginal reconstruction.
► Dissection of the skin-muscle-fat flap is performed taking into account nerve and blood vessel density.
► Distinctive recommendations for the postoperative patient management are given.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The article aids to pay special attention to patients with secondary vaginal atresia and an opportunity for stenosis prevention.
► The introduction and study of secondary vaginal atresia can improve female sexual life and psychological well-being.
► Widespread use of the Martius-Symmonds flap may become part of the standardized recommendations in treatment of secondary vaginal atresia.
Secondary vagina atresia is a quite rare pathology, and due to its low incidence, the lack of standardized recommendations for the management of this group of patients, as well as the insufficient number of relevant randomized trials, the analysis of individual clinical cases is of special relevance. An analysis of the clinical case of a female patient with acquired vaginal atresia underwent surgical treatment – vaginal reconstruction with a Martius-Symmonds flap is presented. In dynamics, after the surgical intervention, good healing and autograft adaptation were noted, without necrosis and ulceration in the area of Martius-Symmonds flap transplantation, with neovagina sized up to 6.5 cm long and 3 to 4 cm wide in different localization. Due to the lack of standardized recommendations for management of patients with acquired vaginal atresia, it is necessary to continue examining and discussing such cases in clinical practice.
FROM HISTORY
The article presents the historical background and professional achievements done by François Morisot, an outstanding French obstetrician from the 17th century who played a key role in the development of modern obstetric science. The authors recount significant events in Morisot's life and career at the Hotel-Dieu de Paris maternity hospital, emphasizing the importance of Dr. Morisot's seminal work “Diseases of pregnant women and postpartum women”, which formed the foundation for obstetric education at that time. Moreover, we also discuss Morisot's innovative practical approaches, including his description of the first ectopic pregnancy, use of manual aids for breech presentations and his technique for puncturing the amniotic sac in cases of bleeding. In addition, Dr. Morisot's critical attitude towards cesarean section and his emphasis on the importance of deep knowledge on anatomy and physiology are additionally noted. Overall, François Morisot's has substantially contributed to the field and his impact has everlasting importance to medical science and obstetric practice.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2500-3194 (Online)