EDITORIAL
The articles in the current issue consider the features of premenstrual syndrome influencing a risk of postpartum depression, organ-preserving methods for treating uterine fibroids as well as examine hemostasis parameters after surgical treatment of endometriosis and an effect related to folic acid on methionine metabolism. Special attention is paid to rare cases such as migraine in hereditary thrombophilia and pregnancy-related antiphospholipid syndrome as well as congenital clitoromegaly and hemodynamic activation of hemostasis in children with heart defects. Innovative approaches to the treatment of female infertility due to endocrine changes and the role of coenzyme Q10 in reproductive medicine are presented. Diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for patients with oncological diseases in the context of pregnancy are also discussed. In addition, the section "From history" covers the cultural and mythological aspects related to Саesarean section.
ОRIGINAL ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
► The incidence of depressive disorders in the postpartum period comprises 10–15 %, with precise causes remaining unclear. It’s not excluded that one of them is the hormonal restructuring that begins immediately after childbirth.
► Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and postpartum depression (PPD) can affect a female health at different time points throughout life. There may be a link between PMS and PPD because both conditions are related to hormone levels. However, interplay is poorly understood.
► Depressive disorders are underestimated postpartum issues. An association between this pathology and certain premorbid conditions cannot be excluded. It has been suggested that PMS may be one of the essential risk factors that remained a bare assumption until we conducted the current study.
What are the new findings?
► This article establishes a link between the occurrence of PPD and PMS, a putative marker of dyshormonal conditions even before conception.
► The article provides a clear understanding about existing relationship between PPD and PMS, also identifying modifying factors that influence severity and duration of such postpartum pathology. It is shown that the most important factor is presented as severity of premenstrual dysphoric disorder.
► Analysis of questionnaire and psychological test results from postpartum women stratified by parity and postpartum period allowed to confirm a overt yet previously scientifically not justified crosstalk between PMS and PPD.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The revealed correlation between PPD and pre-existing PMS allow for its timely prevention and more effective treatment.
► The identified link between PMS and PPD occurrence may shed light on underlying mechanisms for such complication of pregnancy to allow applying more effective pathogenetic treatment modalities and shorten recovery period in postpartum women.
► The psychological diagnostic methods applied in this work can be used to identify PPD risk groups and to prevent this pathological condition.
Aim: to identify a possible association between postpartum depression (PPD) and symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Materials and Methods. A total of 296 women who completed pregnancy to delivery initially agreed to participate in the cohort study, 260 completed the entire survey. All the women, who agreed to take part in the study, were offered three questionnaires. The first questionnaire was collected on day 7–10 postpartum, the second – in 6 weeks and the third – in 6 months after delivery. These questionnaires contained questions of the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale (EPDS) and special questions identifying pre-pregnancy signs of PMS, as well as some lifestyle and medical history questions.
Results. Of 296 participants, 7.1 % had retrospectively identified symptoms of PMS, with 2.7 % showing severe symptoms of premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). In the total cohort, there was a direct correlation between previous PMS and PPD occurring on day 7–10, 6 weeks and 6 months postpartum. After parity separation, this association remained statistically significant only in the multipara cohort.
Conclusion. The relationship between the presence of PMS and the development of PPD has been established. Parity can be considered a catalyst for this relationship. The discovered relationship is particularly important for predicting the occurrence of PPD, as well as for a deeper understanding of the pathogenesis, timely diagnosis, prevention, and choice of treatment methods for this complication of the postpartum period.
What is already known about this subject?
► Uterine fibroids (UF) are benign hormone-dependent myo-
metrial growths.
► Selective progesterone receptor modulators (SPRM) can be used for pathogenetic UF therapy.
What are the new findings?
► The most prominent effect was observed after SPRM therapy course 1.
► According to the histological principle, the lack of fibroids regression after SPRM therapy may raise a suspicion about peculiarities of formation and development of fibroid nodes.
► Selective uterine artery embolization (UAE) accessed through the radial artery optimizes this micro-invasive method of UF treatment.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The use of SPRM as preoperative treatment allows to replace myomectomy to less invasive UAE.
► Conservative and surgical approaches for UF treatment should not be opposed but complement each other to achieve better clinical outcomes.
Introduction. Uterine fibroids (UF) are benign monoclonal hormone-depended tumors originating from smooth myocytes of cervix or body uterus affecting up to 29 % of women aged 15–45 years worldwide. Taking into account the current demographic situation and annually increasing tendency for pregnancy planning at older reproductive age, an organ-sparing strategy is becoming a first-priority approach for UF treatment.
Aim: to investigate efficiency of selective progesterone receptors modulators (SPRM) for UF treatment in women of reproductive age.
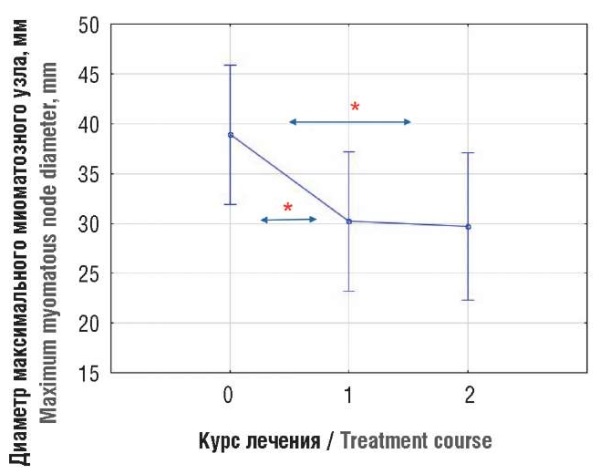
Materials and Methods. A prospective cohort study involved 40 patients with UF at average age of 39.3 ± 5.8 years. Using simple randomization, the patients were divided into 2 groups per 20 women in each. The average age of the patients was comparable and comprised 38.15 ± 5.65 and 40.5 ± 5.8 years in groups 1 and 2, respectively (p = 0.203). In both groups, after assessing liver function tests in accordance with the instructions, a treatment course with SPRM group drug (ulipristal acetate) was used at a daily dose of 5 mg for 84 days (one course) with an interval until the onset of second menstruation after drug withdrawal. Group 1 and group 2 received 2 and 3 therapy courses, respectively. After each course, patients underwent control ultrasound examinations (UE) by analyzing uterus volume and diameter of dominant myomatous node along with liver tests. A temporal quantitation of the difference between UF and dominant node two sizes as well as the maximum uterine volume size and effect size assessment was expressed as the difference of means (Δ) with a 95 % confidence interval (CI).
Results. Based on UE data, the uterus size in group 1 was enlarged to an average of 129.49 ± 75.57 cm3, the maximum size of dominant node was 38.90 ± 17.38 mm; in group 2, the uterus was as large as 294.83 ± 161.37 cm3 with maximum size of the dominant node of 53.33 ± 25.48 mm. After therapy in group 1, dominant node size significantly regressed: after therapy course 1 an effect size of quantitated difference between UF two sizes and the dominant node (Δ) was 8.70 (4.11; 13.29) mm (p < 0.001). After therapy course 2 vs. therapy course 1, a size stabilization (Δ) was noted comprising 1.00 (–1.39; 3.39) mm (p = 0.390); the total effect (Δ) was 9.67 (–14.59; –4.75) mm (p < 0.001). In group 2, after therapy course 1, the dominant node also regressed, with effect size (Δ) of 9.49 (7.08; 11.89) mm (p = 0.001). The effect (Δ) after therapy course 2 vs. therapy course 1 in group 2 was more prominent reaching 10.74 (5.86; 15.61) mm (p = 0.001). However, after therapy course 3, a larger node size was observed compared to therapy course 2 – (Δ) 8.25 (0.67; 15.83) mm (p = 0.329). Despite the lack of pronounced negative dynamics, based on medical indications 9 patients in group 2 underwent uterine artery embolization to prevent disease relapse.
Conclusion. SPRM therapy can be used both as an independent means for UF therapy and in combination with surgical interventions. Such an approach allows for some women to become pregnant without preceding myomectomy, whereas for those approaching age-related menopause to avoid surgical treatment and gently enter natural postmenopause. Currently, conservative and surgical treatment methods for leiomyomas should complement each other to achieve the best clinical outcomes.
What is already known about this subject?
► Endometriosis is a chronic disease characterized by outgrowth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus.
► Endometriosis is accompanied by developing coagulopathy.
What are the new findings?
► External genital endometriosis (EGE) is accompanied by subclinical course of thrombogenesis.
► Coagulopathy in EGE could be managed with corrective treatment.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► A comprehensive evaluation of hemostasis biomarkers may allow for better monitoring of patients' condition after EGE-related surgical treatment.
► Dynamic assessment of von Willebrand factor and D-dimer levels may profoundly improve accuracy of determining hemostasis system status.
Introduction. Endometriosis is one of the common diseases with poorly elucidated underlying nature and pathogenetic mechanisms. Clinical trials suggest that women suffering from it have hemostasis disorders. However, the severity of relevant changes and their origin remain debated.
Aim: to study the dynamics of hemostasis system parameters in patients underwent surgical treatment of external genital endometriosis (EGE).
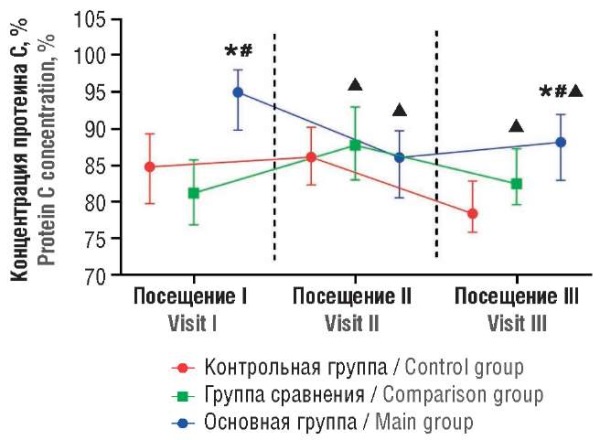
Materials and Methods. A total of 120 women were enrolled into the prospective interventional comparative controlled study: 40 patients with EGE scheduled for surgical treatment (main group), 40 patients with other benign gynecological diseases requiring surgical intervention (comparison group), and 40 apparently healthy women (control group). Нemostasis system status was assessed based on the results of 3 visits during 3 month-follow-up by assessing the following biomarkers: metalloproteinase ADAMTS-13 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13), von Willebrand factor (vWF), D-dimer, protein C, antithrombin III (AT-III), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) and Рarus-test values.
Results. Prior to surgery, among EGE women a subclinical but significant increase in procoagulant biomarkers was observed compared to other groups: vWF – 1.24 [1.17–1.35] U/ml, D-dimer – 173.5 [73.5–221.23] ng/ml. Evaluation of the remaining parameters showed no clinical significance of the observed changes. The endometriosis-related surgical intervention was accompanied by increase in specific procoagulant factors a week post-treatment apparently associated with surgical manipulations. However, 3 months later, hemostasis system status partially normalized as revealed by lower biomarkers examined, which in some cases were significantly decreased compared to those observed before surgery. At the same time, differences between the study groups remained statistically significant.
Conclusion. Patients with EGE were noted to have a subclinical risk of thrombogenesis. Upon this, surgical treatment and rehabilitation during recovery period allowed to improve overall state of the hemostasis system, thereby reducing a thrombogenesis risk.
What is already known about this subject?
► Most studied polymorphisms in MTHFR gene, c.665C>T and c.1286A>C, cause moderate hyperhomocysteinemia (HHC) in folic acid deficiency. Normalizing folic acid level in this pathology normalizes plasma homocysteine (HC) to the optimal level.
► There are synthetic and reduced folic acid (5-MTHF) counterparts. Hypothetically, 5-MTHF overcomes metabolic defects caused by MTHFR gene polymorphism, therefore, its use has advantages over synthetic folic acid. However, no large-scale studies have been carried out to confirm this assumption.
► Over 30 years, women in many countries consume foods fortified with synthetic folic acid according to national programs. However, there are concerns regarding long-term effects linked to unmetabolized folic acid, which remain under investigated.
What are the new findings?
► For the first time, an experimental model with Wistar rats is used to evaluate folic acid supplements and its derivatives on methionine metabolism.
► The experimental model with Wistar rats showed no advantages of 5-MTHF over synthetic folic acid in lowering HC level in plasma and folic acid accumulation in erythrocytes.
► Chronic non-folate-dependent HHC developed in experimental rat models by chronic oral methionine was not reversed by folate supplementation. Сonversely, we found that HC level increased in blood plasma.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Assessing folate status before using different folate preparations may be necessary to avoid excessive accumulation of folic acid and adverse effects on female metabolic systems.
► Chronic non-folate-dependent moderate HHC requires a detailed study of the folate status and proper women’s lifestyle to avoid unnecessary folate administration.
► Our experimental model showed that optimal nutrition of Wistar rats and addition of folates did not result in folic acid accumulation in erythrocytes and blood plasma. Fortification of foods with synthetic folic acid may exert mixed effects.
Introduction. Currently, folic acid preparations are administered during preconception period in an empirical manner. Along with synthetic folic acid, there also exists its reduced counterpart 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF). Manufacturers of the latter claim that 5-MTHF overcomes metabolic defects due to c.665C>T gene polymorphism in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), and therefore it is superior to synthetic folic acid (pteroylmonoglutamic acid, PGA). However, no large-scale studies to confirm this hypothesis have been conducted yet.
Aim: to assess an effect of various folic acid preparations on methionine metabolism in experimental models with Wistar rats.
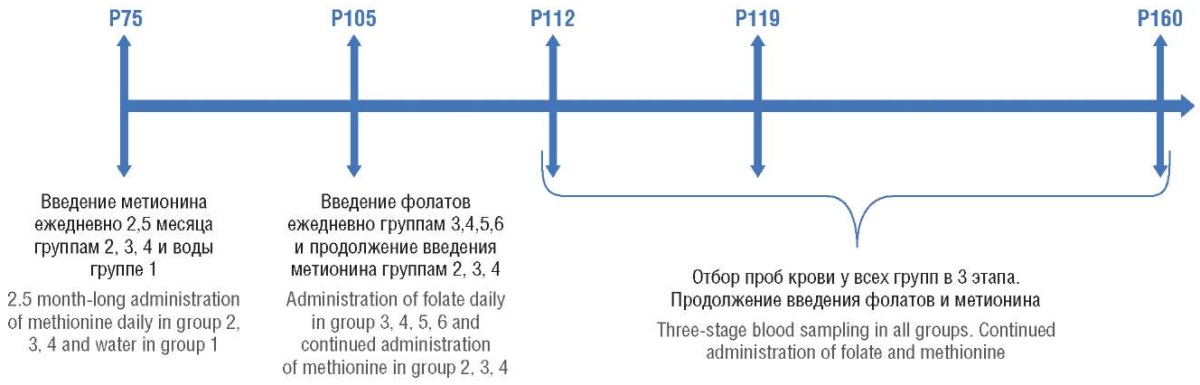
Materials and Methods. A chronic hyperhomocysteinemia (HHC) was induced in sexually mature female Wistar rats by daily methionine supplementation. After HHC development, experimental animals were administered PGA or 5-MTHF. Some animals without HHC also received folic acid supplements or water. Blood samples were collected at 3 time points (1, 2 weeks and 1.5 months after folate preparation administration) to quantitate level of homocysteine (HC), plasma folic acid and red blood cell count.
Results. It was verified that HHC developed in mature Wistar rats after methionine supplementation, with HC level being significantly higher (p < 0.05) than in control group. Use of folic acid supplements during HHC caused by methionine load did not result in lower HC level. In experimental animals administered PGA or 5-MTHF, blood serum folic acid level and red blood cell count did not change upon longer drug administration. No advantage for 5-MTHF vs. synthetic folic acid on HC levels and erythrocyte folate accumulation was observed. Instead of the expected decline in HC level in HHC models related to the examined folate preparations, the opposite effect was obtained. In case of pre-existing non-folate-dependent chronic HHC, HC level increased from time point 1 to time point 3.
Conclusion. Chronic non-folate-dependent HHC, induced by chronic oral methionine was self-limiting in experimental models; additional folate supplementation resulted in sharply increased plasma HC level. Experimental models with Wistar rats showed that no further accumulation of folic acid occurs upon its optimal levels in plasma and red blood cells. The study revealed no advantages for 5-MTHF over synthetic folic acid in lowering blood plasma HC level and folic acid accumulation in erythrocytes.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
► Migraine is one of the most common forms of primary headache. Patients with migraine have an increased risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and hereditary thrombophilia (HT) resulting in pathological pregnancy are highly associated with migraine.
► Migraine is a potential risk factor for pregnancy-related hypertensive disorders.
► Hypercoagulation occurs during pregnancy and coexistence of migraine with APS and HT elevates a risk of developing cardiovascular complications many fold. To date, no clear clinical-diagnostic criteria for migraine in APS and HT were identified.
What are the new findings?
► The article presents the latest research results on safety of pharmacological therapy for management and prevention of pregnancy-related migraine.
► The use of prophylactic treatment for high risk of thrombotic complications in pregnancy-related thrombophilia is accompanied by alleviation or marked regression of migraine headaches especially after using anticoagulants.
► A 2–4-week course of antithrombotic therapy is required for antiphospholipid antibody-positive patients with refractory migraines.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The presence of migraines in the medical history, regardless of phenotype is an important issue while assessing obstetric risk during pregnancy management. Neurologists diagnosing migraines should inquire about the patient's obstetric history.
► Collaboration between neurologists and obstetricians-gynecologists is necessary for timely diagnostics and monitoring of such patients.
► In everyday clinical practice, the effectiveness of antithrombotic therapy in managing refractory migraines should be taken into consideration that underlies its wider use. The results of studies investigating a potential for preventing migraine attack to avoid adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with former migraine hold promise.
Introduction. Migraine is one of the most common primary headaches and a risk factor for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and hereditary thrombophilia (HT) causing pathological pregnancy are highly associated with migraine. Timely migraine recognition related to APS and HT facilitates earlier initiation of thrombophilia pathogenetic therapy and prevention of potential complications.
Aim: to analyze the literature data on migraine clinical and diagnostic features in APS and HT as well as pregnancy-related therapeutic issues.
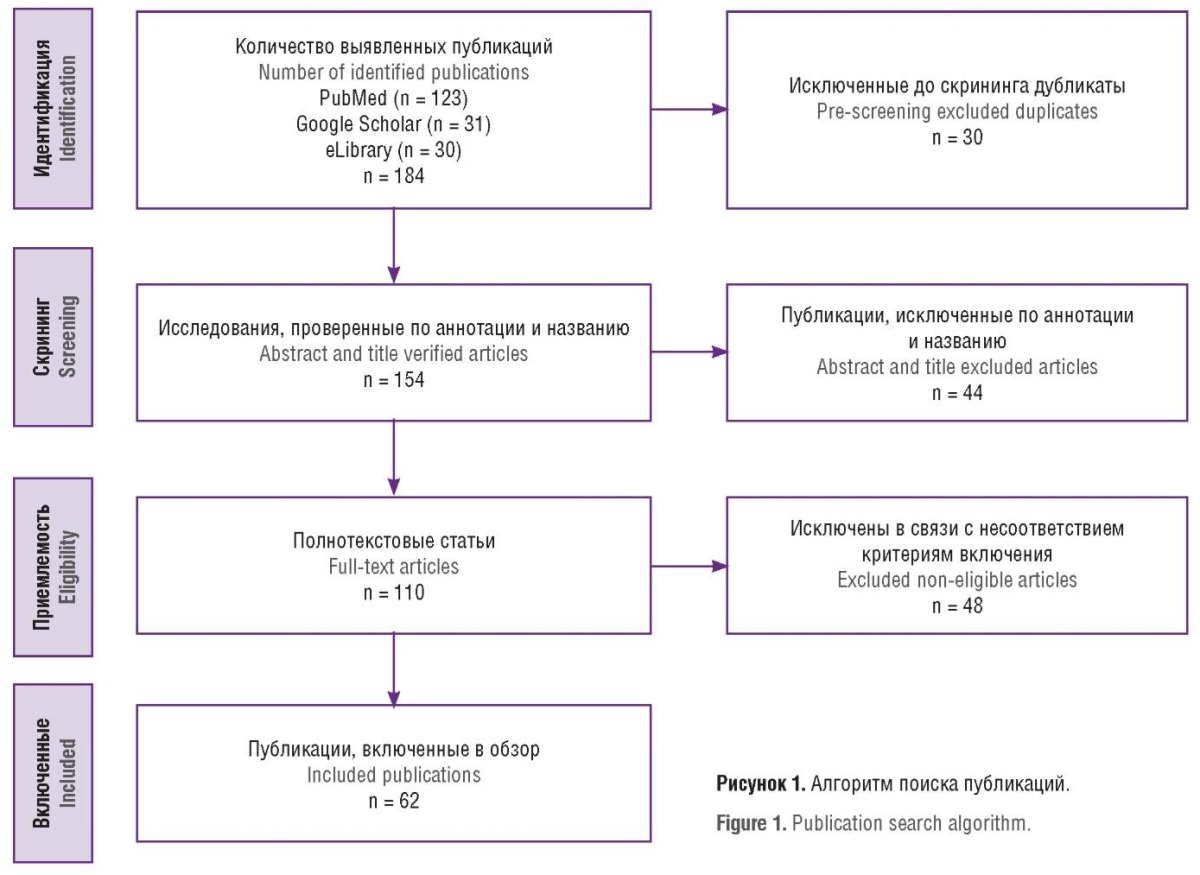
Materials and Methods. A search for scientific literature was conducted in electronic databases including PubMed, Google Scholar, eLibrary from 2004 until May 2024. The search methodological basis included the presence of the following keywords and their combinations in Russian and English: "migraine", "antiphospholipid syndrome", "thrombophilia", "migraine and pregnancy", "migraine and thrombophilia", "migraine and cardiovascular diseases". As a result, a total of 184 publications were identified. Next, 62 articles were included in the review.
Results. At the current stage, neurologists have no means to diagnose migraine in APS and HT based on headache-intrinsic characteristics. Pregnancy increases a risk of thrombotic complications. A migraine observed in patient's history should be crucial while assessing pregnancy-related obstetric risk. While diagnosing migraine, neurologists need to examine patient obstetric history. The data on most effective and safe therapy for pregnancy-related migraine attacks remain scarce.
Conclusion. The frequent association between APS and HT with migraine, the lack of clear migraine clinical features in thrombophilia, patients’ reproductive age, and the high risk of thrombotic complications necessitate collaboration between neurologists and obstetricians-gynecologists for timely diagnostics and management of such patients. The impact of various types of antithrombotic therapy on migraine course requires further clarification. It is promising to conduct studies able to determine of whether migraine attack prevention can avoid adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with former migraine.
What is already known about this subject?
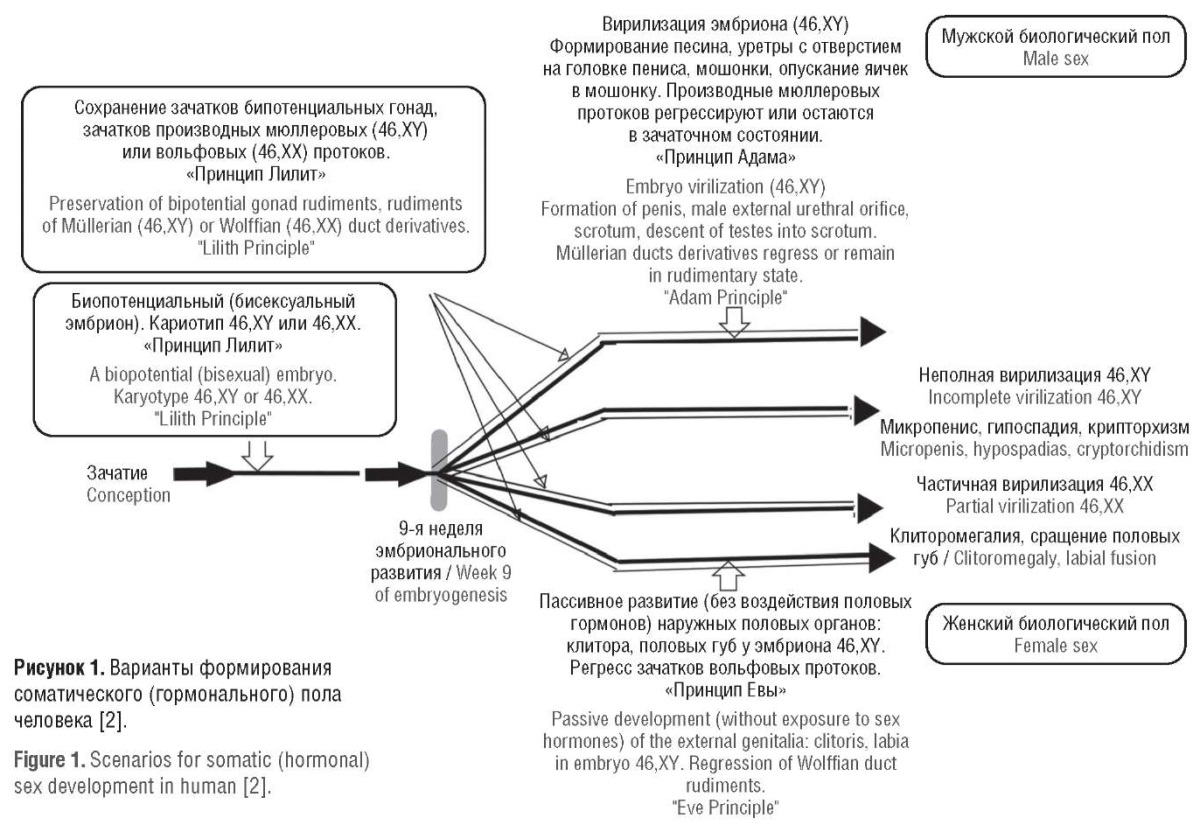
► Clitoromegaly is a common symptom in endocrinological diseases: from nosologies related to disorders of sex formation to virilizing forms of adrenocortical cancer and polycystic ovary syndrome. However, the mechanisms underlying clitoromegaly development are often understudied.
What are the new findings?
► The mechanisms resulting in hyperandrogenism and development of clitoromegaly in patients associated with classical forms of congenital adrenal cortex dysfunction are discussed.
► The role of disturbed androgen synthesis in the adrenal glands and placenta in emerging hyperandrogenism in individuals with karyotype 46,XX is elucidated within the framework of understanding a role of alternative androgen steroidogenesis and mechanisms for 11-oxygenated steroid hyperproduction.
► A role of aromatase in mother's placenta for developing clitoromegaly is analyzed.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► This review suggests expanding diagnostic approaches in management of patients with clitoromegaly to develop effective methods for its prevention and treatment.
Clitoromegaly is characterized by enlarged clitoris exceeding normal size typical to healthy women that represents a pressing issue in gynecological endocrinology. It emerges as an idiopathic condition or is formed along with impaired synthesis of sex steroids, accompanied by androgen excess. However, idiopathic clitoromegaly is a rather common diagnosis, since the objective cause of this symptom often remains unidentified. Investigating an alternative pathway for the synthesis of androgens and 11-oxysetroids in women with clitoromegaly is of great interest to practicing endocrinologists and gynecologists due to new opportunities for diagnosing and preventing this condition. This literature review is aimed at assessing current insights into disorders of female androgen steroidogenesis and its role in clitoromegaly pathogenesis.
What is already known about this subject?
► Von Willebrand factor (vWF) is a multimeric glycoprotein produced in endothelial cells, stored in Weibel–Palade bodies long-term and secreted into the plasma upon endothelial cell activation and damage.
► Metalloproteinase ADAMTS-13 produced in the liver cleaves vWF glycoprotein to low-domain forms, thereby reducing its prothrombotic potential.
► High blood flow velocity leads to vWF conformational changes and transformation of its globular form into a linear counterpart. Domains available for interaction with platelet glycoprotein GpIb receptors account for platelet adhesion and aggregation on the endothelium.
What are the new findings?
► This article demonstrates current data about the domain structure of vWF and metalloproteinase ADAMTS-13, mechanisms of vWF activation in pediatric obstructive congenital heart diseases (CHD) and in univentricular hemodynamics as well as relevant substrate specificity.
► For the first time, we provide a discussion on the mechanisms behind changes in the vWF/ADAMTS-13 axis during obstructive CHD.
► A significance of angiopoietin 1/angiopoietin 2 axis in developing perioperative bleeding as well as vWF/ADAMTS-13 axis in emerging thrombosis has been substantiated.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Lowering a thrombosis risk is impossible without understanding underlying mechanisms. We identify the mechanisms accounting for changes in vWF/ADAMTS-13 axis in various CHD forms.
► Understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms leading to affected vWF/ADAMTS-13 axis in obstructive CHD forms may facilitate application of therapy aimed not only at preventing bleeding, but also thrombotic complications in clinical practice.
► Examining cellular and molecular mechanisms of hemostasis changes should be personalized, since an imbalance between vWF and ADAMTS-13 activity can occur not only in conditions of high-velocity blood flows, but also in patients with univentricular hemodynamics.
Quite complex and non-linear cellular and molecular mechanisms underlie hemostasis changes in patients with congenital heart diseases (CHD). Altered activity ratio between von Willebrand factor (vWF) and metalloproteinase ADAMTS-13 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13) is of pathogenetic significance. The high rate of vWF exocytosis, emergence of its multimeric soluble plasma forms and high rate of proteolysis to small counterparts along with ADAMTS-13 consumption lead to a affected the vWF/ADAMTS-13 axis resulting in hemostasis-related prothrombogenic potential. vWF activity depends on the hydrodynamic characteristics in intravascular blood flow. The magnitude of shear stress in CHD promotes a high rate of conformational changes in vWF multimer, thereby suggesting that hemodynamic conditions may determine developing hemostasis alterations.
What is already known about this subject?
► Female infertility associated with endocrine disorders includes conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome, hypothyroidism, and hypothalamic-pituitary axis disruptions, leading to anovulation and implantation issues, complicating a potential to conceive and sustain pregnancy.
► Endocrine disorders cause hormonal imbalances, anovulation, and disruption of menstrual cycle regulation, leading to in-
adequate endometrial preparation for implantation and pregnancy maintenance.
► Correction of endocrine disorders in women with related infertility results in recovery of hormonal balance, normalized menstrual cycle, and increased odds for successful conception.
What are the new findings?
► The application of cutting-edge biotechnologies in the diagnostics and treatment of endocrine disorders includes gene editing able to affect hormonal balance. Personalized therapeutic approaches based on the patient's genetic profile are proposed allowing for profoundly improving treatment efficacy and minimizing side effects.
► New pharmacological agents primarily targeting endocrine pathways, enhance the effectiveness of ovulation stimulation and improve conditions for implantation.
► The implementation of integrative treatment approaches combining traditional methods with innovative technologies and the optimization of treatment protocols enhance the effectiveness of infertility treatment.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The implementation of genetic profiling will allow more precise selection of treatment methods based on individual patient characteristics.
► New pharmacological agents and technologies for targeted impact on endocrine pathways will help to increase the efficiency of in vitro fertilization (IVF).
► Оptimization of treatment protocols will help reduce the overall costs of infertility treatment, shortening duration and number of required IVF attempts.
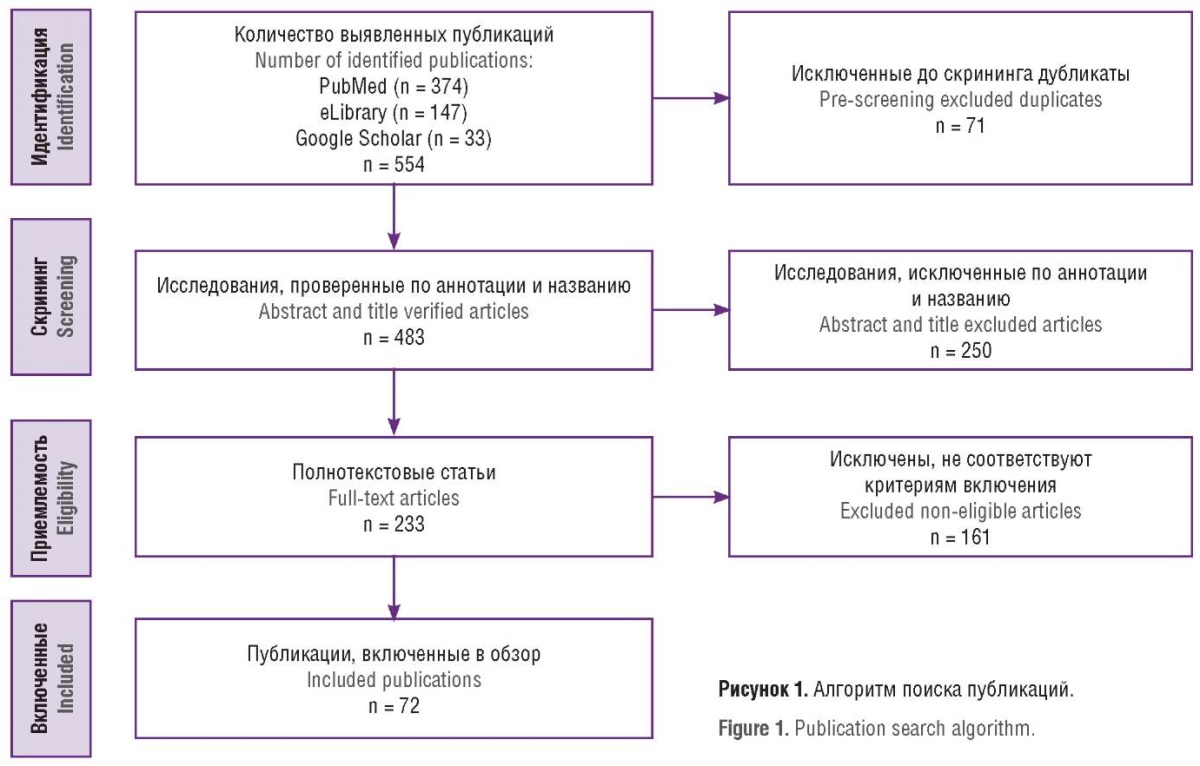
Aim: to analyze the publications assessing innovative methods of diagnostics and treatment used to solve the problem of female infertility associated with endocrine disorders.
Materials and Methods. There was conducted a search for publications in electronic databases PubMed, Google Scholar, and eLibrary, which were selected in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. All relevant articles published up to January 2024 were included in the review. As a result, 374 publications retrieved from PubMed, 147 – from eLibrary, and 33 – from Google Scholar were extracted. Duplicates and non-full-text versions of articles were excluded. After the selection procedure, 72 publications were included in the review.
Results. During the data analysis, we identified key aspects providing deeper understanding of endocrine disorders affecting female infertility. In particular, new correlations were demonstrated between the level of select hormones and treatment success, as well as pathogenetic mechanisms were also identified influencing the conception and pregnancy process. These results will allow to develop more accurate diagnostic criteria and effective treatment methods able to increase women's chances of successful conception and pregnancy.
Conclusion. The data analysis identified the hallmark aspects for diagnostics and treatment of female endocrine infertility, with new diagnostic criteria and effective treatment methods identified able to markedly improve outcomes. The crucial potential of the innovative approaches and methods considered contributes to improving reproductive health and increasing the chances of successful conception. We strongly encourage the introduction of such advanced technologies into clinical practice to optimize reproductive success.
What is already known about this subject?
► Coenzyme Q10 (СоQ10) plays an important role in embryonic development, participating in oxidative phosphorylation and electron transfer in mitochondria. It is a key link in the ATP synthesis chain, providing energy to cells in developing organism.
► СоQ10 exerts antioxidant properties, protecting cells from the harmful effects of free radicals, which is primarily important for embryogenesis when tissues and organs are at the formation stage.
► Exogenous CoQ10 supplements have antioxidant effects and may be a potential therapy to alleviate oxidative stress.
What are the new findings?
► In the absence of CoQ10, ATP synthesis declines in parallel with elevated oxidative stress in mitochondria, two biological events that affect embryonic development.
► CoQ10 deficiency markedly increases the risk of impaired embryonic development.
► Excessive CoQ10 level can lead to altered embryonic development.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Normalization of CoQ10 level will help to avoid developmental abnormalities and associated termination of pregnancy.
► CoQ10 reduces the frequency of preeclampsia by participating in the formation of the placenta and can also improve the quality of eggs and gametes and reduce other developmental abnormalities.
Maternal mitochondria provide energy to the embryo through oxidative phosphorylation before blastocyst implantation, where intracellular energy is mainly supplied by glycolysis. Thus, it is obvious that mitochondria play a crucial role in providing energy for embryogenesis. Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a powerful endogenous membrane-localized antioxidant that protects circulating lipoproteins from lipid peroxidation. The results of several recent clinical studies have shown that exogenous CoQ10 supplements exert antioxidant effects and may be a potential therapy to reduce oxidative stress. CoQ10 deficiency increases the risk of impaired embryonic development; however, this relationship remains unclear. Given that CoQ10 level is influenced by enzymes involved in its synthesis, it is difficult to say whether the disorders are caused by CoQ10 deficiency or directly result from defects in the target gene. It has been shown that in the absence of CoQ10, ATP synthesis decreases in parallel with increased oxidative stress in mitochondria, two biological events which affect embryonic development. The review highlights the importance of CoQ10 as an antioxidant for improving egg quality, and also emphasizes its key role in embryonic development. It is necessary to conduct further studies aimed at studying metabolic changes during embryogenesis, as well as the mechanism of CoQ10 effects.
CLINICAL CASES
What is already known about this subject?
► Metastatic breast cancer (ВС) is a heterogeneous group of diseases with varying clinical manifestations. Both solitary (single or oligometastatic) as well as multiple, or diffuse, lesions are observed.
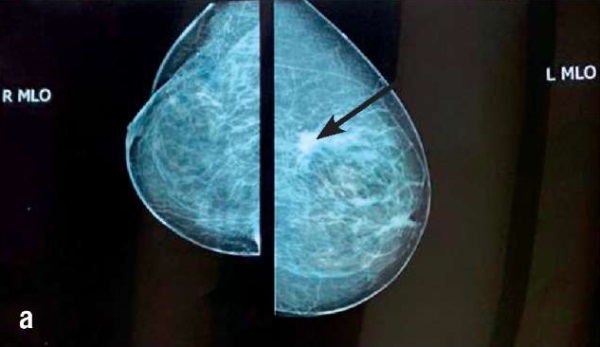
► In 3 % of ВС women radiologic findings include a solitary shadow in the lung recognized as a metastatic lesion. BC metastasis to the lung tissue comprises 21–32 % distant metastasis cases leading to fatal outcome in 60–70 % of cases.
► When the size of pulmonary node is less than 1 cm or its anatomic location is unfavorable for diagnostic testing, surgical intervention is required to confirm pathomorphologic diagnosis.
What are the new findings?
► The therapeutic and diagnostic algorithm for patients with diagnosed ВС and focal peripheral lung neoplasm is presented.
► The role of surgical intervention such as videothoracoscopic lung resection with urgent histologic examination for diagnosis verification and determining neoplasm morphologic composition was demonstrated.
► A two-stage surgical strategy was developed to exclude the secondary lung neoplasm with subsequent removal of the primary focus.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Application of the proposed therapeutic and diagnostic algorithm in clinical practice will optimize and improve the quality of treatment for patients with diagnosed ВС and focal peripheral lung neoplasm.
► The use of such surgical tactics will allow morphologic verification of single focal masses in the lungs with unfavorable anatomic location for diagnostic puncture.
► Exclusion of secondary lesions in patients with diagnosed ВС will avoid unnecessary cardio-, hepato- and nephrotoxic chemotherapy.
Breast cancer (BC) has long held a leading position in oncology disease pattern among global female population. Statistics data show that BC metastasis to lung tissue accounts for 21–32 % of all distant metastasis cases. Pulmonary metastases usually occur within 5 years after initial BC diagnosis, more often affecting peripheral lung parts, which explains the difficulty for their differential diagnosis. In addition, they profoundly impact on disease course and patient survival rate, so that each case of combined pathology such as BC and lung solid neoplasm is of interest in terms of clinicopathologic features as well as the diagnostic approach, with subsequent choice of surgical treatment tactics. Obviously, a therapeutic strategy in such cases is based on knowing primary tumor morphological structure and verifying metastatic process. However, in case of small sized pulmonary focus, it is difficult to identify a modality of ongoing process. Currently, no therapeutic and diagnostic tactics in such cases have been developed in detail. Assessing the clinical case of a combined ВС and a single small-sized focal lung mass, we propose an effective diagnostics and treatment scheme.
What is already known about this subject?
► Early-onset neonatal sepsis (EОNS) caused by Proteus mirabilis (P. mirabilis) is extremely rare.
► P. mirabilis-caused EОNS is most often associated with death or development of severe neonatal brain abscesses.
► A few reports of such cases are available worldwide, and none of them was described in Russia.
What are the new findings?
► The article provides the first description of EОNS clinical case caused by P. mirabilis in Russia.
► A summary of the existing global data on this issues and a detailed description of the clinical case are presented.
► The features of intraamniotic infection course in tetrachorial triamniotic triplets are presented.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The presented clinical case will remind that EОNS etiology is more diverse than usual.
► The article may allow to timely suspect etiology of P. mirabilis-caused infectious process.
► The chosen etiotropic therapy tactics and relief of multiple organ failure may be an example on providing care to patients with this disease due to favorable outcome.
Early-onset neonatal sepsis (EОNS) is one of the most severe diseases of the neonatal period and is often coupled to extremely unfavorable outcomes. In many ways, the severity of the condition and the results of newborn nursing depend on the etiology of the bacterial process. The major EОNS pathogens are traditionally considered to be Streptococcus group B and E. coli, much less common are other Gram-negative bacteria including casuistic cases caused by caused by Proteus mirabilis (P. mirabilis). The article provides a review on the P. mirabilis role in developing neonatal sepsis with pathogen-specific disease course and outcomes. In addition, we describe a clinical case of P. mirabilis-caused EОNS not only primarily characterized by the rarity of its causative agent, but also that it proceeded with a more favorable brain damage in contrast to similar cases described worldwide and because the neonatal EОNS developed in one of triplets, with two other babies being asymptomatic despite that P. mirabilis was also detected.
What is already known about this subject?
► Breast cancer (ВС) in pregnant women is a rare pathology in practice of an obstetrician-gynecologist and the most common among oncopathology in pregnant women.
► ВС is not an indication for pregnancy termination.
► Current therapy interventions allow to successfully treat BC provided that pregnancy is prolonged by giving a chance for survival and a joy of motherhood.
What are the new findings?
► The article is intended to draw an obstetrician-gynecologist’s attention providing primary outpatient health care to ВС issue in pregnant women.
► The clinical case described additionally confirms a promise of treating ВС and maintaining pregnancy.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Knowing such clinical case will increase cancer awareness regarding > 35 year-old pregnant women with cancer risk factors such as ВC in first-second-lineage female relatives, late childbirth.
► Mandatory and thorough breast examination in pregnant women upon registration, ultrasound examination at the end of the first pregnancy trimester will allow to timely suspect cancer, correctly design and implement an algorithm of therapeutic diagnostic measures to achieve a favorable outcome.
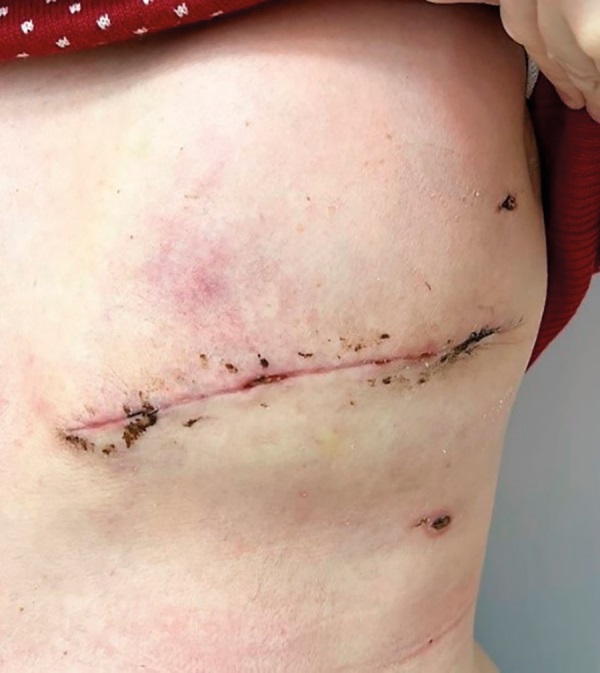
Pregnancy-associated breast cancer (ВС) is a rare pathology in the practice of an obstetrician-gynecologist and oncologist, which diagnostics is coupled to certain difficulties. The joint efforts of specialists to solve this issue taking into account current diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities are aimed at achieving a positive outcome. A clinical case of invasive hormone-dependent ВС T4bN3aM0, IIIC associated with pregnancy presented here is to outline a typical scenario of the following disease course: tumor manifestation in the second trimester, mastitis-like form, late diagnostics. The latter may result from low oncological alertness towards pregnant women under the age of 40 years old due to the rarity of such pathology. The proper decision-making of drug therapy algorithm according to the verified tumor histological variant and immunohistochemical status along with surgical treatment allowed not only to achieve tumor regression, give birth to a healthy full-term baby, but also gave a chance for survival despite late-onset treatment. To avoid advanced disease progression, it is advisable to recommend ultrasound breast examination in the first trimester for pregnant women over 35 years of age.
FROM HISTORY
Caesarean section is one of the ancient and most outstanding operations, with roots going deep into the past. It shows unmatched significance in that it is the only operation responsible for the lives of two people – mother and child. Hypotheses about the origin of the term a Сaesarean section, the history of its development and methods underlying execution the operation are discussed here. The article highlights issues aimed at Сaesarean section in fine art, the historical stages of this operation and their reflection in fine arts. Studying artistic works related to Caesarean section helps us to better understand its impact on mankind and social consciousness.
EVENTS
СORRIGENDUM
The authors regret regret that the published version of the article contains an error in Figure 1. We present the correct Figure 1. We are sure that the error made could not have significantly affected the perception of the material and the interpretation of information by readers. The error has been corrected in the electronic form on the journal's website, the article file has been updated.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2500-3194 (Online)