ОRIGINAL ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
► COVID-19 and cancer are associated with a higher risk of thrombotic complications that further potentiates upon their combination.
► Both conditions cause hypercoagulability and increased thrombogenicity.
► Anticoagulant therapy is effective in lowering thrombotic risk.
What are the new findings?
► Cancer patients with COVID-19 experience elevated von Willebrand factor (vWF) level and metalloproteinase ADAMTS-13 deficiency.
► An early severity criterion in this case may be proposed as a vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio exceeding 2.1.
► A prominent rise in ADAMTS-13 inhibitor level was observed in Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients, especially in non-survi-
vors being a sign for progression of systemic inflammatory response syndrome, despite of anti-inflammatory therapy.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The study provides deeper insight into the impact of COVID-19 on cancer patients, which may influence treatment strategies in this patient group.
► Assessing vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio as an early indicator of disease severity can assist in early diagnostics of thrombotic complications and potentially life-threatening conditions.
► The study data highlight a need for continuing investigations to propose more precise treatment protocols and predict a risk of thrombosis in cancer patients with COVID-19.
Aim: to study the features of thrombotic complications in cancer patients during COVID-19 infection, and identify the most significant diagnostic and prognostic criteria.
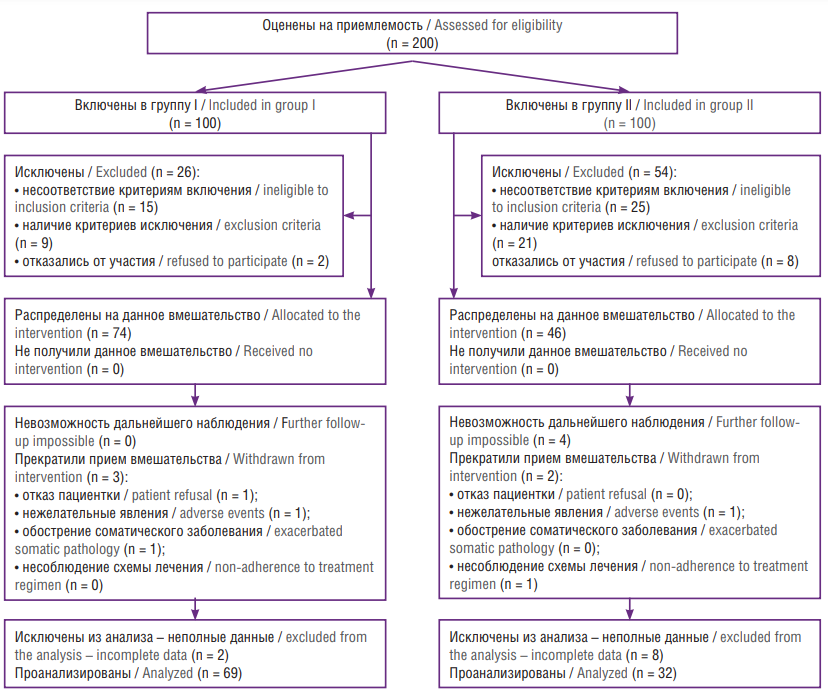
Materials and Methods. Within the framework of cohort non-randomized study, there were analyzed the course of coronavirus infection in 72 hospitalized patients with uterine cancer (n = 22), cervical cancer (n = 19), ovarian cancer (n = 24) as well as vaginal and vulvar cancer (n = 7). All patients hospitalized for COVID-19 were examined and treated in accordance with the Interim guidelines “Prevention, diagnosis and treatment of novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19)” effective at the time of therapy. Additionally, on days 3–7 after hospitalization, a blood test was performed once to determine the level of metalloproteinase ADAMTS-13 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13), ADAMTS-13 activity, ADAMTS-13 inhibitor and von Willebrand factor (vWF) level.
Results. It was shown that the average age of the patients was 56.96 ± 7.55 years, the length of hospitalization ranged from 7 to 19 (13.0 ± 3.79) days. The disease severity was assessed by the degree of lung tissue damage based on computed tomography (CT), respiratory failure and development of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). During hospitalization, CT-2 was detected in 46 (63.9 %) patients, CT-3 – in 26 (36.1 %) patients; 37 (51.4 %) patients were transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU). Clinically significant deep vein thrombosis (DVT) was diagnosed in 9 (12.5 %) patients, and pulmonary embolism (PE) – in 4 (5.6 %) patients. Of these, 6 cases of DVT and 3 cases of PE were fatal. A total of 14 (19.44 %) patients deceased due to developing acute cardiopulmonary failure. A vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio greater than 2.1 was found in all ICU patients. Despite anticoagulant therapy, patients with DVT and PE had this ratio higher than 3.3 (4.00 ± 0.48), whereas in all 14 deceased patients it exceeded 2.98.
Conclusion. Venous thromboembolism, including PE and DVT, has been identified as а serious complication of COVID-19. An opportunity to predict them early is of special importance because they may lead to serious complications such as disseminated intravascular coagulation, SIRS, cardiopulmonary failure, and death. In patients suffering from cancer infected with COVID-19, not only a decline in ADAMTS-13 activity and level was detected, but also a parallel increase in vWF level. A vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio may be an early indicator of COVID-19 severity in such patients: a vWF/ADAMTS-13 ratio exceeding 2.1 was common for all ICU patients. Hence, it evidences about a potential for using this parameter to early identify such risk patients who may require more intensive care and medical intervention.
What is already known about this subject?
► Most often, premature birth (РВ) is caused by an infection.
► Altered microbiomeis observed in one third of pregnant women.
► Treatment of vaginal dysbiosis during pregnancy most often relies on antibacterial agents.
What are the new findings?
► The relationship between РВ risk and the combinationt reatment of bacterial vaginosis using antimicrobial peptides and cytokines has been shown.
► No recurrent vaginosis was found in pregnant women after combination treatment.
► A combination treatment was proved to lack any negative effect on neonates’ condition.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Reducing risk and recurrence of bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy.
► With a decrease in the frequency of РВ, a decrease in material costs and psychological costs of disorders in married couples is expected
Introduction. The prevalence of bacterial vaginosis (BV) comprises 23–29 %, which in pregnant women is a known risk factor for premature birth (PB) that rates increases by 2.9-fold. BV treatment with antibiotics has no effect PB incidence, therefore stressing a need to search for alternative remedies.
Aim: to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, including antibacterial therapy and a complex preparation containing natural antimicrobial peptides and cytokines, to reduce the incidence of birth defects in pregnant women with BV.
Materials and Methods. Design: a prospective open comparative cohort study in parallel groups was conducted with 101 pregnant women: Group I (n = 69) received the antibiotic Metronidazole, 500 mg tablets orally twice a day for 7 days, and a complex preparation containing exogenous natural antimicrobial peptides and cytokines (Superlymph®) suppositories per 25 IU once a day vaginally in the evening for 20 days; Group II (n = 32) received Metronidazole alone (the same regimen). Patient examination was carried out using approaches included clinical methods, accepted in obstetrics, and laboratory tests – microscopy of vaginal content smears, real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Results. The PB (within 240–366 weeks) incidence in Group I was significantly lower than in Group II and comprised 2.9 % vs. 21.9 %, respectively (p = 0.004), with an 8-fold decline in developing PB risk (relative risk (RR) = 0.13; 95 % confidence interval (CI) = 0.03–0.60), whereas inter-group percentage of pregnant women with high risk (PB history) was comparable (p = 0.39) so that PB incidence did not differ from pregnant women without former PB. Microbiological recovery after treatment for BV was achieved in 85.5 % of patients from Group I vs. 56.3 % in Group II (RR = 1.52; 95 % CI = 1.10–2.10; p = 0.002) based on real-time PCR data. The persistence of anaerobic flora after treatment was significantly lower in Group I vs. Group II reaching 7.2 and 34.4 % (p < 0.001), respectively, with a 5-fold lower PB risk (RR = 0.21; 95 % CI = 0.08–0.56). Cessation of viral shedding compared to the number of patients with initial viral shedding was achieved in 94.6 % vs. 8.3 % of patients, respectively, with a 50-fold decline in risk (RR = 0.02; 95 % CI = 0.005–0.08; p < 0.001). The number of newborns weighing less than 2500 g was significantly lower from paired mothers who received Superlymph® + Metronidazole comprising 2.9 % vs. 15.6 % treated with Metronidazole alone (p = 0.03), whereas a risk of low birth weight neonates was decreased by 6-fold (RR = 0.16; 95 % CI = 0.03–0.88). The condition of the neonates assessed by birth Apgar score was comparable.
Conclusion. The use of a complex preparation Superlymph® (suppositories per 25 IU once an day vaginally, for 20 days) along with oral antibiotic Мetronidazole in pregnant women with BV facilitates a decline in PB incidence down to 2.9 % at gestational age of 240–366 weeks lowering a risk of PB exceeding that of antibacterial therapy by 8-fold, including patients with former PB.
What is already known about this subject?
► Preeclampsia (РЕ) is a multifactorial pathology and resulting from collective effect of various factors (genetic, epigenetic, immunological, environmental, etc.).
► At present, there is a search mainly tending for anamnestic, clinical and biochemical predictors of PE development particularly biomarkers available in practice to be used to predict PE development and severity in early pregnancy.
► Given the wide functional miRNAs potential, an active research field is to seek out for and identify new molecules involved in РЕ development.
What are the new findings?
► РЕ has been shown to be characterized by specific molecular changes at the transcriptome level.
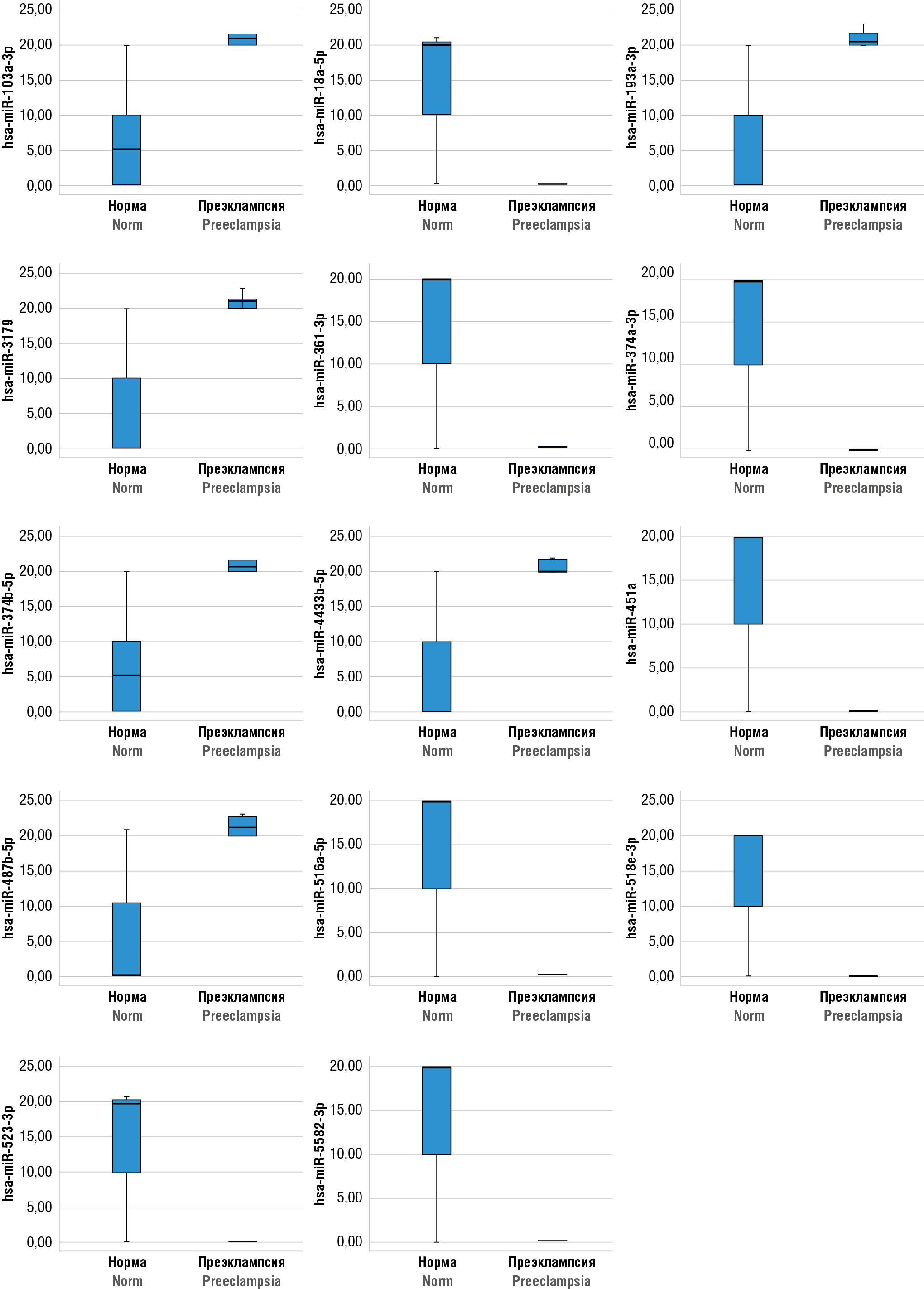
► It has been established the high prognostic value for hsa-miR-103a-3p, hsa-miR-451a and hsa-miR-516a-5p involved in РЕ pathogenesis.
► A prognostic РЕ developmental model was put forward based on the clinically most significant differentially expressed plasma microRNAs.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► MicroRNAs are promising biomarkers with good diagnostic potential for implementation in a screening program to predict РЕ and can be used as a sensitive indicator for clinical prediction of pregnancy complications.
► The developed logistic model can be used for prediction and early РЕdiagnostics able to reduce obstetric complications and improve perinatal outcomes.
Aim: to develop a model for predicting preeclampsia (PE) based on the clinically most significant differentially expressed plasma microRNAs.
Materials and Methods. A prospective observational comparative study was conducted with 62 women, divided into two parallel groups: 32 patients with PE and 30 clinically healthy women with uncomplicated pregnancy. Transcriptomic analysis was performed to identify differentially expressed blood plasma microRNAs using next generation sequencing (NGS).
Results. Calculation of risk ratios for PE development allowed to identify 14 plasma microRNAs that influence the development of PE pathology. PE-associated microRNAs hsa-miR-103a-3p, hsa-miR-451a and hsa-miR-516a-5p have a high diagnostic value when combined to assess their blood plasma expression level in early pregnancy stages.
Conclusion. The developed prognostic model can be applied to pregnant women at risk for PE development, which may further reduce obstetric complications and improve perinatal outcomes.
What is already known about this subject?
► Pelvic organ prolapse (РОР) holds the third place after benign neoplasms and endometriosis among causes of gynecological diseases.
► Surgical correction of defects in the fascial structures of the pelvic floor is the main method for РОР treatment. However, the rate of post-surgery POP relapse reaches 30 %.
► The expansion of young, socially and sexually active patient population with POP prolapse accounted for increased demands for the effectiveness and safety of surgically treated pelvic floor muscle failure.
What are the new findings?
► MESH bilateral sacrospinous fixation (SSF) via anterior approach was shown to be a clinically effective method able to result into a significant reduction in prolapse relapses, early and long-term complications.
► Anterior bilateral SSF allows to lower frequency of patient complaints about urination disorders, aids to alleviate pain severity and shorten length of hospital treatment.
► Improved РОР surgical treatment via anterior bilateral SSF was demonstrated to ensure better dynamics of pelvic organ parameter dysfunction, patients' overall quality of life and quality of sexual life.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The approach proposed allows to minimize patients’ complaints, rate of complications and РОР relapses.
► Anterior bilateral SSF with synthetic tape in POP surgical treatment may aid in shortening length of patient hospitalization, alleviate pelvic dysfunction, improves quality of life and sexual function.
Aim: to increase the clinical effectiveness and safety of apical prolapse treatment by applying anterior bilateral sacrospinous fixation (SSF) with a polypropylene mesh implant.
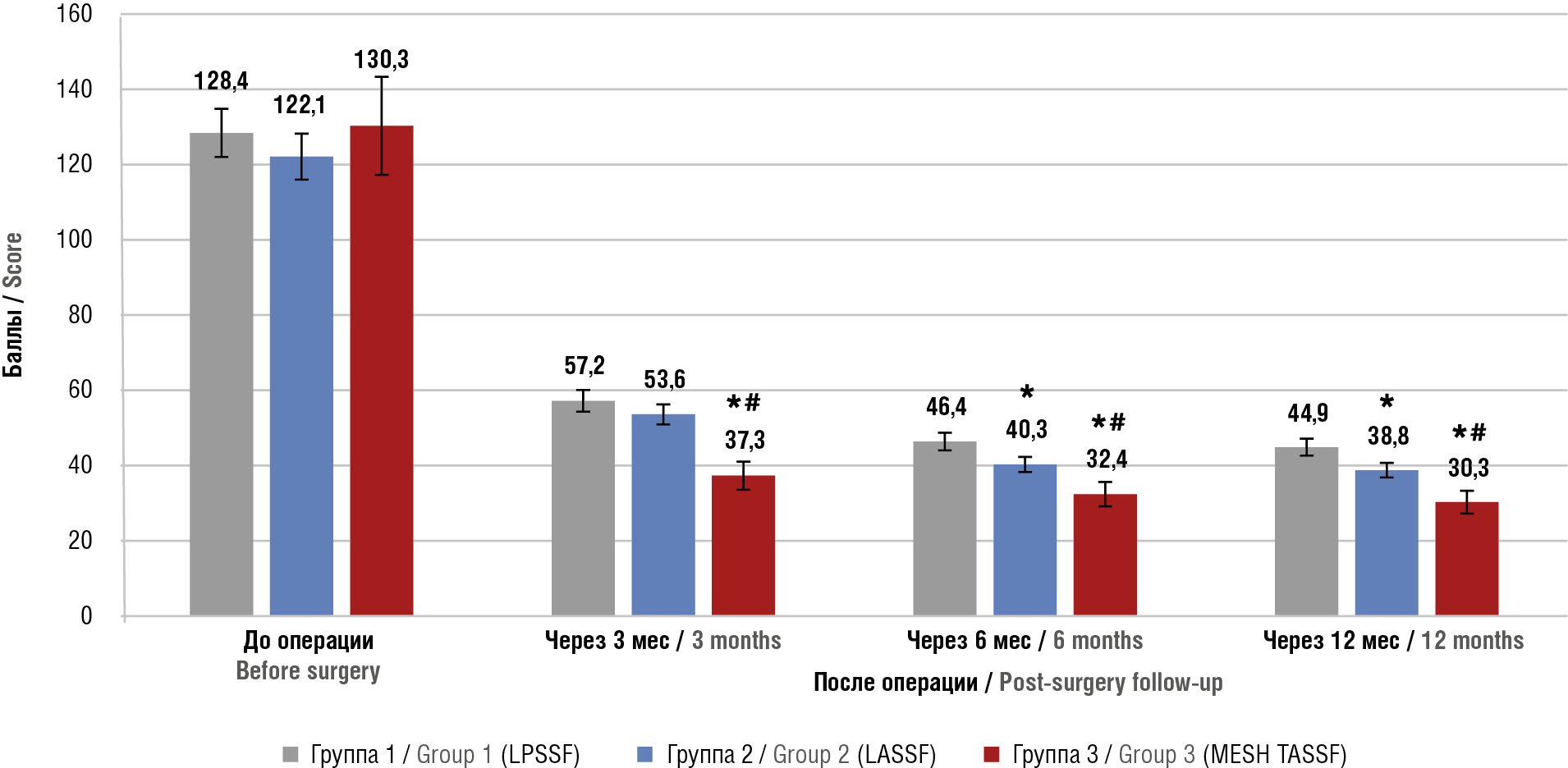
Materials and Methods. A single-center open prospective comparative clinical study in parallel groups in parallel groups was carried out at the Clinic of Academician Krasnopolsky Moscow Regional Research Institute of Obstetrics and Gynecology. There were examined and treated 155 patients with stage II–IV symptomatic genital prolapse according to the Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification System (POP-Q) who underwent various variants of SSF. The patients were stratified into 3 groups: group 1 (LPSSF) – 34 patients with symptomatic apical genital prolapse who underwent SSF through the posterior vaginal wall using LPSSF ligatures (ligature posterior sacrospinous fixation); group 2 (LASSF) – 42 patients with symptomatic apical or anterior-apical genital prolapse, who underwent ligature SSF using the anterior approach LASSF (ligature anterior sacrospinous fixation); group 3 (MESH TASSF) – 79 patients with symptomatic apical or anterior-apical genital prolapse, who were treated by applying the anterior bilateral SSF method using synthetic tape MESH TASSF (tape anterior sacrospinous fixation). The frequency of intra- and postoperative complications, patient complaints, and relapse rates were assessed post-surgery. Functional outcomes were assessed using the PFDI-20 questionnaire (Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory-20) at 3, 6 and 12 months after treatment. Patients in group 3 were treated by applying a method we developed for correction of apical genital prolapse and concomitant cystocele reconstruction.
Results. The method presented here was characterized by a lower blood volume loss compared to posterior SSF, minimized intra- and postoperative complications: decreased incidence of hematomas, buttock pain, rate of urinary disorders (stress incontinence, mixed forms of urinary incontinence, urgent urinary incontinence, urinary difficulty, bladder hypotension). Applying MESH TASSF fixation allowed to decrease duration of hospital treatment and alleviate pain severity in the postoperative period, and additionally contributed to improved patients' quality of life sustained for as long as 12 months post-surgery.
Conclusion. The treatment results confirmed that the MESH bilateral SSF method using an anterior approach is clinically effective, relatively safe, and contributes to a markedly reduced rate of disease relapses. The presence of anterior-apical or apical genital prolapse (C or Ba+C prolapse, stages II–IV according to the POP-Q) should be considered as indications for performing anterior bilateral SSF.
What is already known about this subject?
► Vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA)is the major manifestation of genitourinary menopausal syndrome (GUMS) profoundly lowering the quality of life (QoL).
► There is a gap in long-term comparative controlled studies assessing rehabilitation effect on QoL in patients with VVA of various etiologies.
What are the new findings?
► A personalized rehabilitation program contributes to the improvement of all QoL aspects in patients with VVA, assessed with questionnaires during 2-year follow-up.
► Patients with VVA in surgical vs. natural menopause had more prominent decline in QoL, but recovery occurs faster while using comprehensive "active" rehabilitation.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Introducing into clinical practice an investigated program for comprehensive "active" rehabilitation in patients with VVA will improve the QoL in such patients, positively influencing the outcome.
Aim: to evaluate the impact of rehabilitation on various components of quality of life (QoL) in patients with vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA).
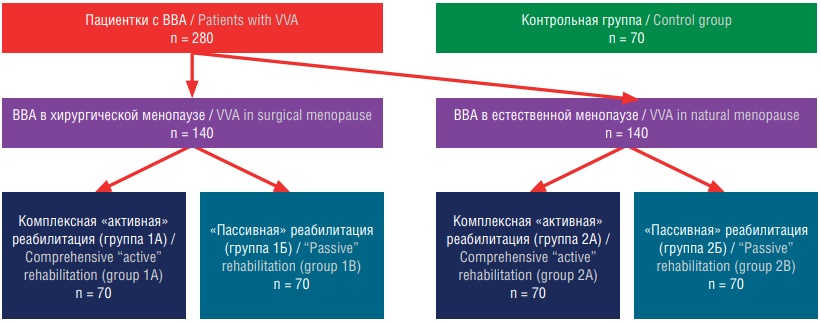
Materials and Methods. A prospective comparative controlled longitudinal study involved 350 patients with VVA, divided into groups based on the type of menopause: surgical (n = 140) and natural (n = 140), with a control group of 70 women without VVA. Patients were further subdivided into those receiving complex "active" (groups 1A, 2A) and "passive" (groups 1B, 2B) rehabilitation. The study included 6 visits over 24 months, assessing QoL using the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), Modified Menopausal Index (MMI), Well-being, Activity, Mood questionnaire (WAM), Magnesium Deficiency Questionnaire (MDQ), and the Assessment Test of Magnesium Deficiency (ATMD).
Results. Women with surgical menopause had severe sexual dysfunction initially. Complex "active" rehabilitation significantly improved sexual function over time compared to "passive" rehabilitation. Surgical menopausal women had higher initial levels of anxiety and depression. "Active" rehabilitation significantly reduced these levels, reaching normal values within the first year. Patients with surgical menopause exhibited more severe menopausal symptoms. "Active" rehabilitation led to significant reductions in these symptoms, improved well-being, activity, and mood more significantly than "passive" rehabilitation, particularly in the first year. Complex "active" rehabilitation normalized magnesium deficiency indicators within three months, maintaining normal levels throughout the study.
Conclusion. Comprehensive "active" rehabilitation significantly improves sexual function, reduces anxiety and depression, alleviates menopausal symptoms, and enhances overall well-being in women with VVA, especially those in surgical menopause. Personalized rehabilitation programs are crucial for enhancing QoL in these patients.
What is already known about this subject?
► Retained products of conception (RPOC) are detected in 10–15 % of patients after spontaneous or medical abortion.
► In RPOC treatment "blind" intrauterine intervention remains "gold standard".
► "Blind" RPOC removal is often associated with the development of certain complications that pose a serious threat to female fertility and quality of life.
What are the new findings?
► The results of comparatively analyzed application of hysteroscopic morcellation (НМ) and RPOC "blind" vacuum aspiration are presented.
► Based on analyzing markers of inflammatory response, endometrial microcirculation in the early post-surgical period, conclusions about the minimum НМ damaging effect on the endometrium, were made able to lower the probability of postoperative adhesion.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► НМ is an effective and safe means to eliminate RPOC and may be a preferred alternative for "blind" intrauterine interventions.
Introduction. Retained products of conception (RPOC) are detected in 15 % of women after spontaneous or medical abortion. RPOC blind removal from the uterine cavity remains the "gold standard" of surgical treatment, which, however, may be associated with a high risk of certain complications that pose a serious threat to female reproductive function and quality of life. An alternative method for eliminating RPOC proposed by operative hysteroscopy demonstrating the visual control advantages.
Aim: to evaluate clinical effectiveness and safety of RPOC removal in incomplete spontaneous abortion using hysteroscopic morcellation.
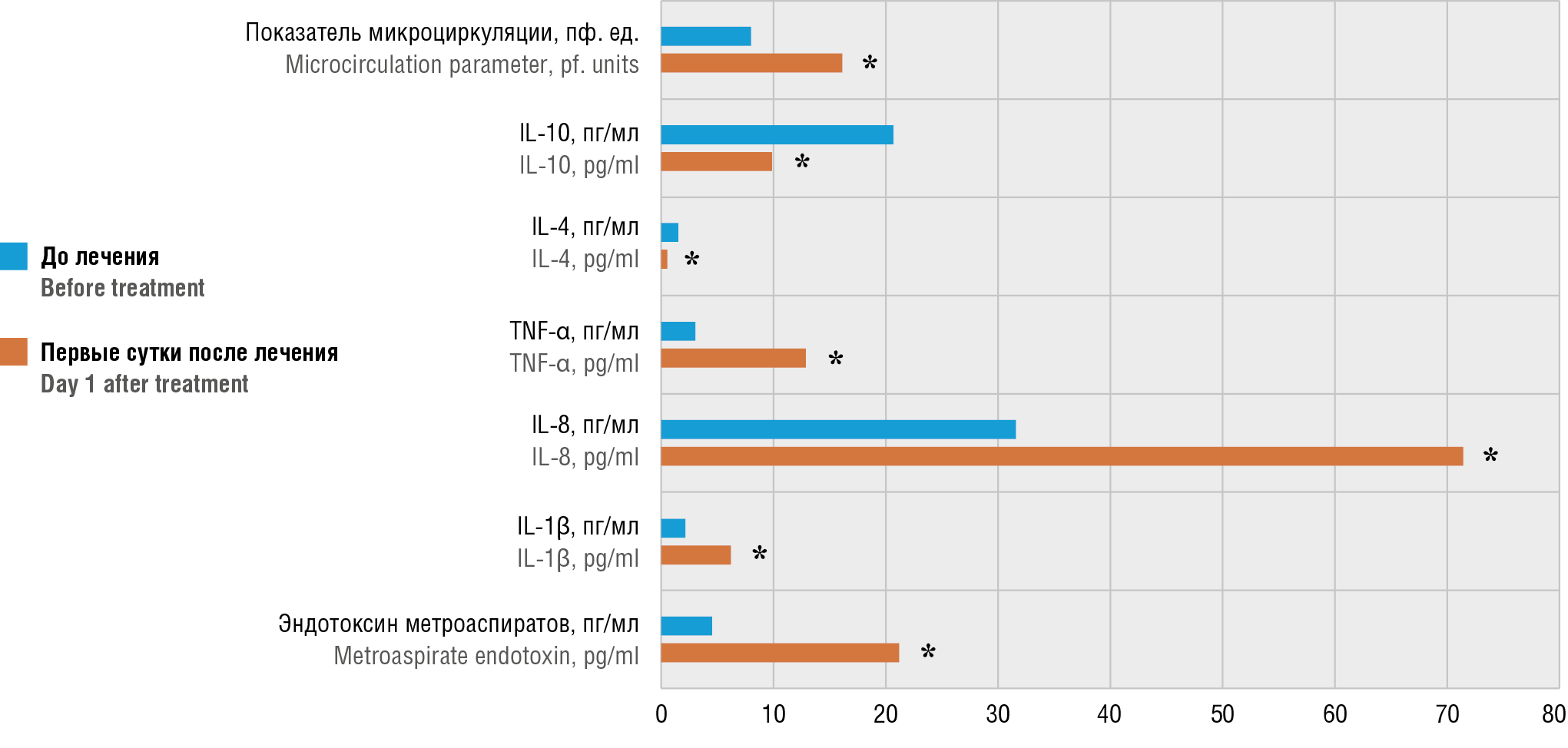
Materials and Methods. The prospective comparative study included 135 women with incomplete spontaneous abortion aged 18 to 40 years, divided into 3 groups: group 1 – 42 patients after RPOC electromechanical vacuum aspiration (EVA); group 2 – 44 patients after RPOC manual vacuum aspiration (MVA); group 3 – 49 patients after RPOC hysteroscopic morcellation (HM). In all patients, the level of total endotoxin was measured, metroaspirate cytokine profile was analyzed, the indicator of endometrial microcirculation was assessed before surgical treatment and on day 1 afterwards, and genital ultrasound examination was performed on day 3–5 post-surgery.
Results. In the post-surgical vs. pre-treatment period, the EVA and MVA groups revealed significantly increased levels of total endotoxin and interleukin (IL) IL-1β (p < 0.05). In contrast, these parameters in the HM group changed insignificantly (p > 0.05). In all groups, IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) levels after surgery were significantly elevated (p = 0.001). In the EVA and MVA groups, levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-10 were markedly decreased (p = 0.001), which did not change in the HM group (p > 0.05). A significantly accelerated microcirculation rate was noted in the EVA and MVA groups while comparing it at pre-surgery level (p = 0.001), but not in the HM group (p = 0.415). Incomplete RPOC removal was reported for 4.5 % MVA patients, all EVA and HM patients had total RPOC elimination. Intraoperative bleeding, uterine perforation were not reported in any examined patient.
Conclusion. The early-stage treatment results showed that RPOC removal by the HM is an effective and safe approach. Limited inflammatory response and stable endometrial microcirculation upon using the HM evidence about a minimal impact on the endometrium that lowers probability of postoperative adhesion.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
► Obstetric hemorrhage is a severe life-threatening complication being one of the leading causes in maternal morbidity and mortality. Proper assessment of bleeding risk factors will allow for more reliable diagnostics, timely prevention and effective treatment tactics.
► Modern advances based on the latest computer technologies have been gaining increasing practical value as tools for calculating risk of obstetric bleeding. Currently, the main objective of multiple research studies in this
field is to seek out for important risk factors with peak impact on emerging bleeding during pregnancy, childbirth
or postpartum period.
What are the new findings?
► Here, we review Russian and international publications revealing the prospects for using machine learning methods to predict obstetric hemorrhages, as well as the data from recent research in this field.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► It is anticipated that the development of predictive models in digital format using machine learning algorithms will open up novel paths to improve accuracy of assessing a personalized risk of haemorrhages. This suggestion is based on the successful domestic and international practice of implementing integrated predictive analytics systems in areas of medicine such as oncology, cardiology, ophthalmology and reproductive medicine.
► Identifying women from the high-risk group will allow for more effective prenatal monitoring and timely delivery, determine a correct mode of delivery and use medications for preventive means or transfer patients to a medical center that provides a higher level of obstetric care.
Obstetric hemorrhages (OH) are the main preventable cause of morbidity, mortality and cases of "near miss" among obstetric complications worldwide. Early preventive measures based on the OH prediction allow to profoundly reduce the rate of female mortality and morbidity as well as prevent the economic costs of patient intensive care, blood transfusion, surgical treatment and long-term hospitalization. Postpartum haemorrhage (PPH) is the most frequent obstetric haemorrhage determined by one of the four causes: a uterine tonus disorder, maternal birth trauma, retention of placenta parts and blood-clotting disorder. There is still a need for the continued search for an accurate and reliable prediction method despite multiple attempts to develop an effective system for predicting OH. The solution to this may be reasonably considered an innovative method such as artificial intelligence (AI) including computer technologies capable of obtaining conclusions similar to human thinking. One of the particular AI variants is presented by machine learning (ML), which develops accurate predictive models using computer analysis. Machine learning is based on computer algorithms, the most common among them in medicine are the decision tree (DT), naive Bayes classifier (NBC), random forest (RF), support vector machine (SVM), artificial neural network (ANNs), deep neural network (DNN) or deep learning (DL) and convolutional neural network (CNN). Here, we review the main stages of ML, the principles of algorithms action, and the prospects for using AI to predict OH in real-life clinical practice.
What is already known about this subject?
► Neonatal thrombosis is a quire rare but serious condition that can be fatal for newborns.
► One of the main risk factors for development of neonatal thrombosis is application of central venous catheters.
► Treatment of neonatal thrombosis is a complex process that requires a personalized approach based on thrombus location, patient health condition and other additional risk factors.
What are the new findings?
► New data on risk factors for neonatal thrombosis are presented, taking into account up-to-date research data.
► The influence of congenital and acquired thrombophilia, thromboinflammation and maternal COVID-19 infection on developing neonatal thrombosis was analyzed.
► New methods for prevention and treatment of neonatal thrombosis are discussed able to assist in lowering neonatal mortality and morbidity.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Implementation of new risk assessment methods for more accurate prediction of developing neonatal thrombosis may prevent it and improve patient outcome.
► Innovative diagnostic approaches described in the article can provide faster and more accurate detection of thrombosis or prethrombotic state, which will allow to apply a proactive treatment and increase therapeutic effectiveness.
► New treatment strategies may lead to revision of approved recommendations for management of patients with neonatal thrombosis.
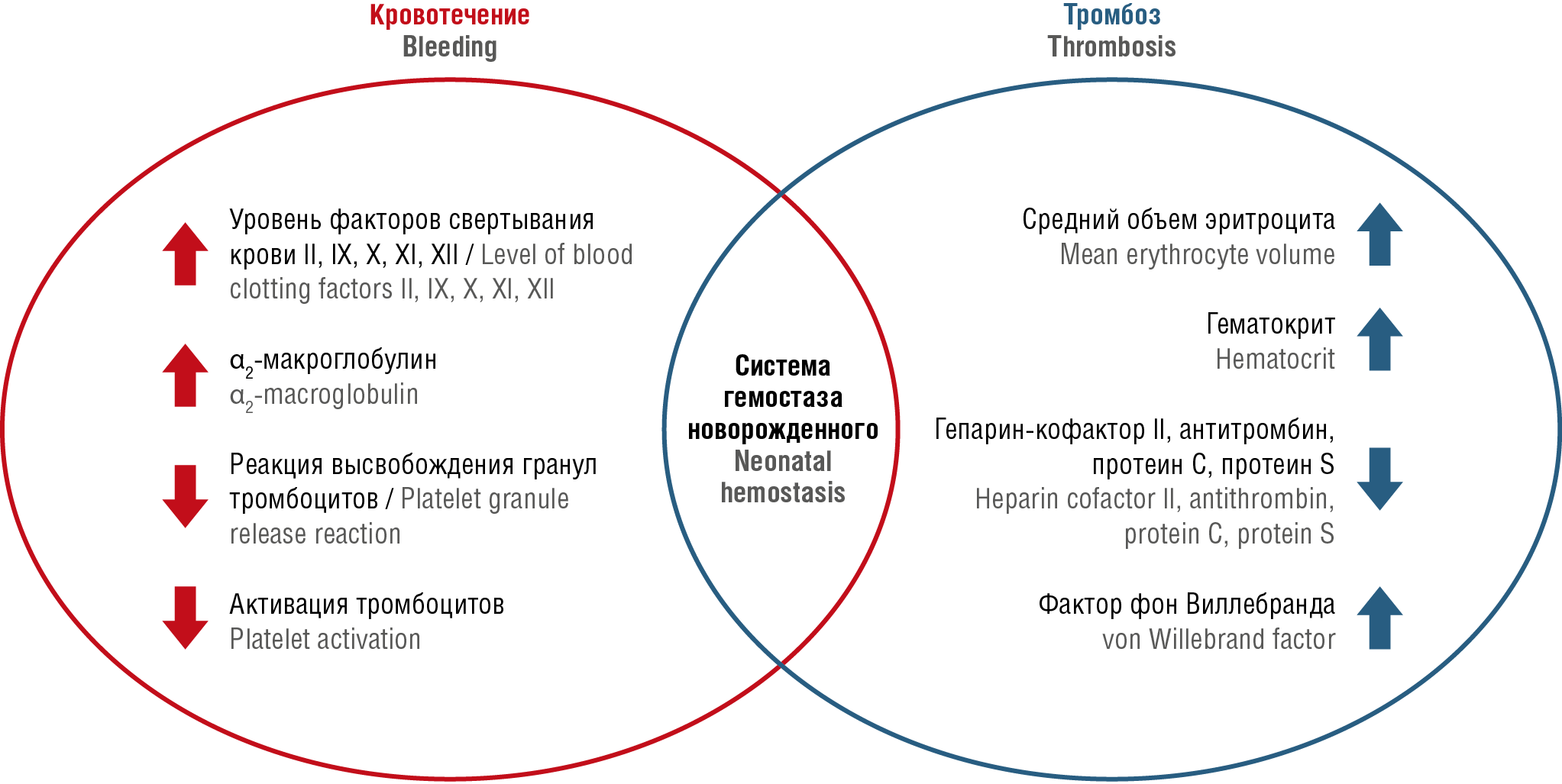
Compared to children of other ages, neonates especially seriously ill and premature subjects comprise a high thrombotic risk group. A decline in the incidence of neonatal thrombosis may be accounted for by improved treatment of severe conditions in newborns and increased survival of premature infants. Neonatal and adult hemostasis exhibit distinct physiological features: difference in concentration, synthesis rate of blood coagulation factors, metabolic rate, thrombin and plasmin levels. At the same time, neonatal threshold values for natural blood coagulation inhibitors (protein C, protein S, antithrombin, heparin cofactor II) and vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors (FII, FVII, FIX, FX) are quite low, whereas that of FVIII and von Willebrand factor exceeds those found in adults. Thus, newborns have lower plasma fibrinolytic activity. The main risk factors for developing thrombotic complications are as follows: central venous catheters, altered body fluid volume, liver disease, as well as sepsis and inflammatory processes particularly COVID-19. The significance of congenital and acquired maternal and neonatal thrombophilia may pose an additional risk factor for thrombotic complications. Low-molecular weight heparins are the first-choice drugs in treatment and prevention of neonatal thrombosis.
What is already known about this subject?
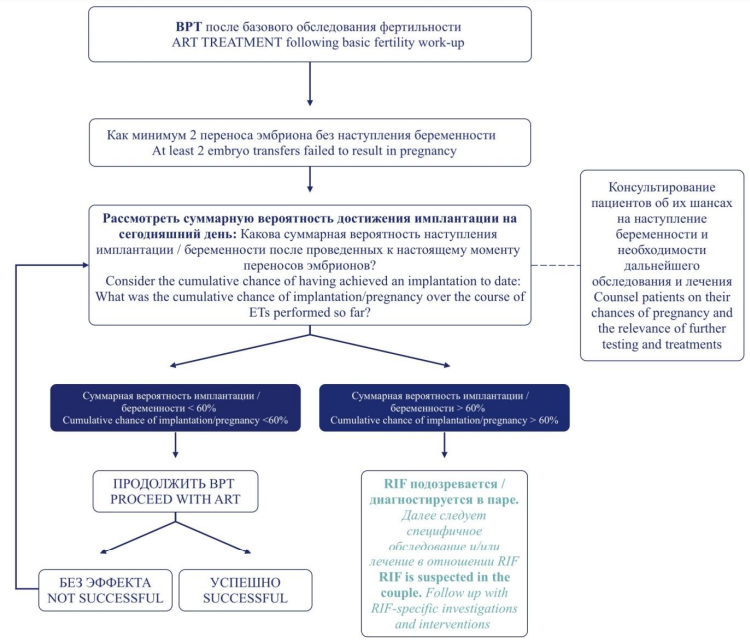
► Repeated implantation failures (RIF) represent a relatively new term that describes a pressing multifactorial issues related to assisted reproductive technologies (ART), widely used at present.
► Potential RIF factors can be classified into those related to female, male, embryo, as well as mixed factors able to complicate diagnostics and comprehensive treatment.
What are the new findings?
► The article summarizes the main female RIF factors (lifestyle, genetic factor, uterine pathology, endometriosis and adenomyosis, thrombophilia), potential mechanisms resulting in RIF, diagnostic issues and currently available treatment options.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Therapy aimed at RIF factors may improve ART outcomes and increase pregnancy and live birth rates.
► An individual approach to RIF-specific examination and treatment will avoid ineffective medical interventions and bring patients closer to long-awaited clinical pregnancy.
Embryo implantation is the first key step in successful pregnancy, but implantation failures remain quite common in patients undergoing assisted reproductive technology (ART) programs. The main known factors of repeated implantation failures (RIF) in patients undergoing ART are unhealthy lifestyle, genetic factor and low gamete quality, uterus pathology, endometriosis and adenomyosis, thrombophilia as well as male factor and embryonic factors. RIF factors and ways to overcome them have received much attention. Despite multiple RIF causes being identified, the underlying etiology and management remain poorly investigated. In clinical practice, studies and interventions providing no clear scientific rationale or convincing evidence on their effectiveness due to the lack of standardized diagnostic and treatment methods that are often used. An effective strategy for treating RIF risk factors is necessary to increase chances for successful pregnancy in ART programs.
CLINICAL CASES
What is already known about this subject?
► Physiological changes that occur in a female body during pregnancy complicate laboratory diagnostics of рrimary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT).
► Being untreated, the incidence of PHPT-related complications in pregnant women, according to various sources, ranges from 14 to 67 %, in newborns – up to 80 %.
► An opportunity of drug therapy for PHPT in pregnant women is limited. The data from recent studies demonstrate the advantage of surgical tactics compared with conservative management in prevention of neonatal complications.
What are the new findings?
► It is advisable to conduct an in-depth examination of women before planning pregnancy and in vitro fertilization (IVF) in case of pathologies associated with impaired phosphorus-calcium metabolism.
► The extremely high risk of complications in PHPT during pregnancy due to IVF requires a special assistance and active interaction between representatives of a multidisciplinary team to chose an optimal treatment tactics aimed at maintaining pregnancy.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► We will propose to introduce a screening assessment of phosphorus-calcium metabolism parameters during preconception period and pregnancy.
Primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT) in pregnant women is a rare condition, often remaining undiagnosed due to non-specific clinical symptoms. However, it can lead to life-threatening complications for both the mother and fetus. In vitro fertilization (IVF) is also associated with an increased probability of adverse outcomes compared to the general population. Timely diagnostics and personalized treatment, taking into account the extremely high risk of complications if PHPT and pregnancy result from IVF, require attention of healthcare professionals and formation of a multidisciplinary team.
What is already known about this subject?
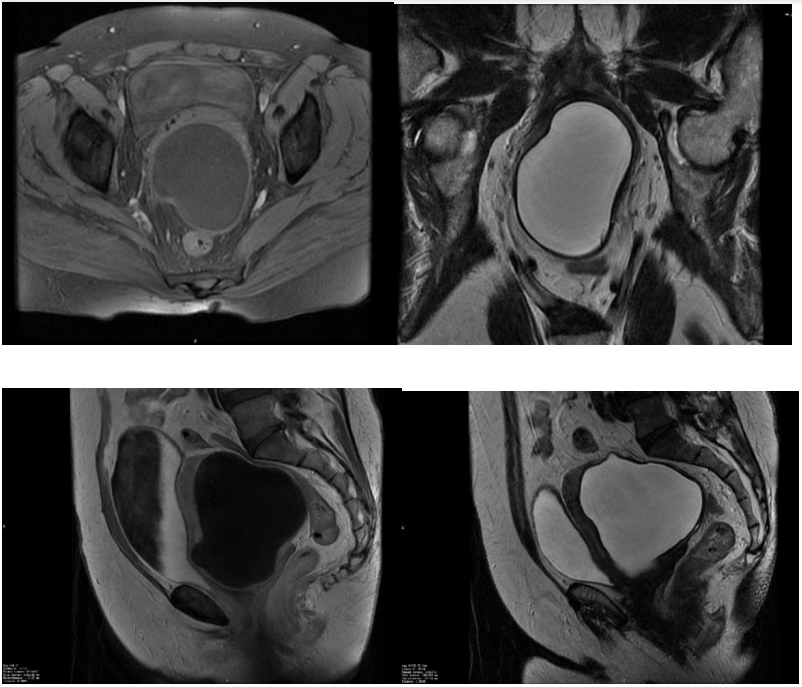
► Hydatidosis is a severe parasitic disease caused by tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus. After the cestodes enter the systemic circulation they can penetrate virtually any organs and tissues.
► The pathogen is commonly localized in organs such as liver (63 %), lungs (25 %), muscles (5 %) and bones (5 %) but also can target other organs, including pelvis in casuistic cases.
What are the new findings?
► The article describes the main algorithms of the differential diagnosis between uterine hydatidosis and gynecological disease based on MRI data.
► Large pelvic echinococcosis cyst may cause serious complication such as relapsing episodes of acute urinary retention due to urethral compression cystic outgrowth. Sometimes, it may represent a sole symptom of the disease.
► Surgical treatment of primary uterine hydatidosis may be potentially complicated by injury of adjacent organs (ureters, intestines, blood vessels) tightly adhered to cyst capsule.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► To avoid complications such as anaphylactic shock and impaired function of adjacent organs, gynecologists and surgeons should be alert about a potential for developing of such rare phenomenon in clinical practice requiring to collect a thorough anamnesis, epidemiological data, conduct laboratory and visualization assays.
► Hydatid cysts of rare localization should be primarily differentiated from benign and malignant neoplasms.
► The current clinical case encourages to think about a need for multidisciplinary approach while treating complicated clinical cases to increase probability of correct diagnostics, choice of proper therapeutic strategy and timely surgical treatment without complications.
Introduction. Hydatidosis is a severe parasitic disease caused by tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus widely spread in some endemic areas all over the world that primarily targets liver, lung, bones, muscles well as pelvis in casuistic cases. Due to the lack of pathognomonic signs as well as low prevalence rate of hydatid cysts in such anatomic sites, a differential diagnosis for relevant gynecological pathologies may be substantially complicated. Compared with common gynecological disease such as uterine fibroids, ovarian cyst and malignancies uterine hydatidosis may be identified only in 0.16 % cases.
Aim: to present a clinical case of uterine hydatid cyst in order to optimize algorithms for differential diagnosis of primary pelvic echinococcosis and gynecological pathology, which is necessary for successfully conducted timely surgical treatment.
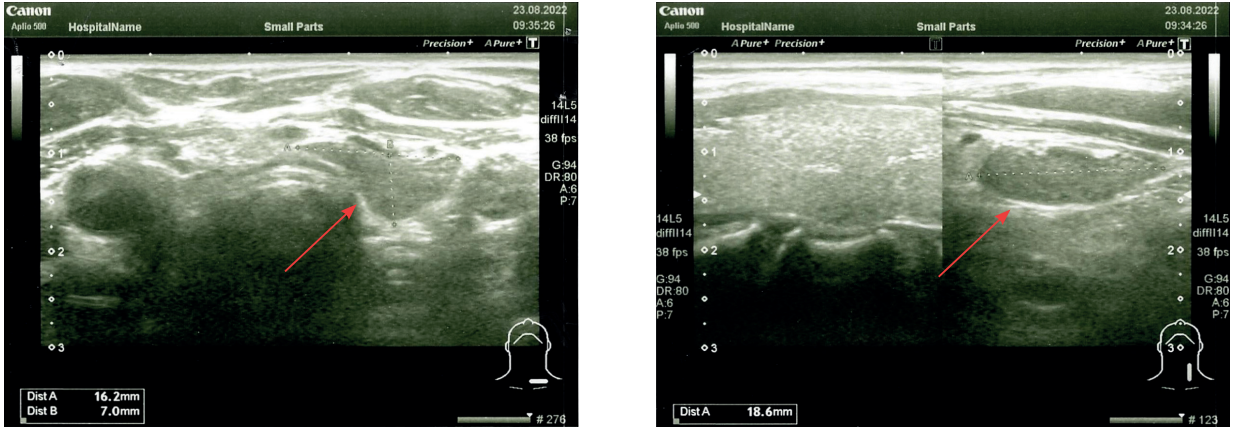
Clinical case. In 2023, patient K. complained of dysuric phenomena and a feeling of heaviness in the pelvic area. Based on the anamnesis, clinical picture, laboratory and instrumental research methods, it was decided to perform surgical treatment. The patient underwent laparoscopic hysterectomy and removal of ¾ hydatid cyst. The obtained material was used for histological examination to verify the diagnosis.
Results. Differential diagnosis of uterine echinococcosis is most often carried out with cystic or dysembryogenetic tumors, purulent or tuberculous abscesses, ovarian cysts, ovarian tumors, and uterine fibroids. Features of the MR picture, such as a thick compacted wall, the lack of internal septa, parietal and papillary outgrowths, as well as a solid component, allowed to suspect parasitic genesis of the neoplasm.
Conclusion. While treating patients with cystic neoplasms of the pelvic area referred from endemic areas, echinococcosis should be included in the list of differential diagnostic searches.
FROM HISTORY
The article highlights issues aimed at maternal death in literature. The literary works of Tolstoy, Turgenev, Bunin, Rabelais, Martin, Pushkin, Mann, etc., are discussed.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2500-3194 (Online)