EDITORIAL
This issue focuses on developing a unified, interdisciplinary approach to obstetrics, gynaecology, andrology and reproductive medicine based on objective data. The aim is to move from making decisions based on experience to using targeted, guided strategies based on early biomarkers and standardized algorithms. The review highlights studies demonstrating a pragmatic approach to life-threatening obstetric conditions, such as the management of coagulopathy in postpartum haemorrhage with a focus on the timely administration of tranexamic acid and the appropriate replacement of fibrinogen. It also covers new methods for combating postpartum infection and the early sepsis prediction. In gynaecological practice, the importance of minimal technological improvements (e.g. local antibiotic therapy during laparoscopy) in improving reproductive outcomes is emphasized, as is the relevance of organ-preserving surgery. There is a particular focus on structuring diagnostic pathways in andrology for azoospermia and oligozoospermia, where integrating spermiological, hormonal, ultrasound and genetic data enables differentiation of pathogenesis and development of personalized treatment strategies ranging from drug therapy to assisted reproductive technologies. The article also discusses the progressive integration of molecular markers (e.g. nectin-4 and components of extracellular vesicles) into clinical practice for diagnosing and prognosing reproductive system cancers, emphasizing the need for standardized analysis methods. The discussion of patient management strategies for menopausal women takes an interdisciplinary approach, requiring collaboration between gynaecologists, endocrinologists and dentists, and emphasizing the importance of preliminary hormonal correction prior to dental implantation. Taken together, the materials provide a comprehensive picture of the contemporary transformation of clinical practice, based on evidence-driven interdisciplinary dialogue.
ОRIGINAL ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
► Patients with infertility and/or recurrent pregnancy loss are at high risk for triggering infectious complications during pregnancy.
► The inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system particularly chronic endometritis (СЕ) are associated with infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss.
► Bacterial colonization and impaired endometrial receptivity are associated with activated proinflammatory mechanisms contributing to implantation failure and/or pregnancy loss.
What are the new findings?
► The comprehensive analysis of anamnestic, clinical and immunological parameters in women with infertility and/or recurrent pregnancy loss is presented.
► The parameters of innate immunity assessed by analyzing gene expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory factors in the scraping of the cervical mucosa found the difference in the messenger RNA (mRNA) expression for interleukin-1β (IL-1β) gene – one of the leading factors involved in the embryonic-
endometrial dialogue – in patients with infertility and a history of recurrent pregnancy loss.
► Difference in expression of IL-1β gene, which encodes one of the main pro-inflammatory mediators, in patients with infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss implies different mechanisms of impairment of embryonic-endometrial dialogue.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The prevalence of СЕ ultrasound signs in women with infertility and/or recurrent pregnancy loss is determined, which in some cases dictates the need for further histologically verified inflammation in mucosal layer and antibacterial therapy.
► Women with a history of reproductive losses with current dysbiotic disorders in lower reproductive tract are extremely required to undergo correction of microbiocenosis before pregnancy, especially in case of chronic endometrial inflammatory pathology with accompanying activation of local immunity (according to the study on innate immunity genes expression).
► The presented data on gynecological, obstetric, reproductive history, mRNA expression of innate immunity genes in women with infertility and/or recurrent pregnancy loss confirm the importance for integrated approach assessing a role of infectious factor in origin of reproductive disorders.
Aim: to conduct a comprehensive analysis of clinical, anamnestic and immunological characteristics of women with infertility and/or a history of recurrent pregnancy loss.
Materials and Methods. A cross-sectional study included 302 women of reproductive age with a history of infertility and/or recurrent pregnancy loss by enrolling those who was planning pregnancy and directed for preconceptional councelling in 2023–2024. Patients were divided into 3 groups depending on whether they had experienced infertility (n = 108), recurrent pregnancy loss (n = 141), infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss (n = 53). The study flowchart included the collection of gynecological and obstetric histories, as well as ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs in follicular phase. Expression of innate immunity gene mRNAs was carried out: interleukins (IL) IL-1β, IL-10, IL-18, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3), cluster of differentiation 68 (CD68), β2-microglobulin. Based on the mRNA expression profiles of the studied genes, the integral inflammation index (II) was calculated automatically using binary logistic regression software. A local inflammatory reaction in the cervical mucosal scraping was recorded when the II value exceeded 60 %. Statistical analysis was performed using R v 4.4.3. In hypothesis testing, differences were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Results. The prevalence of inflammatory endometrial pathology (chronic endometritis diagnosed by ultrasound) was comparable among groups 1, 2, 3 (16.7; 19.9; 18.9 %; p > 0,05). A greater incidence of ultrasound detected intrauterine adhesions was found in group 2 with combined infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss (17,0 %) compared to infertility group 1 (4.6 %; p = 0,022) and comparable to recurrent pregnancy loss group 3 (14.9 %; p > 0,05). Uterine septal removal was performed more often in group 2 (17.0 %) than in group 1 (1.9 %; p = 0,003). Endometriosis was diagnosed more often in group 2 (24,5 %) than in group 3 (7.8 %; p = 0,009). Reproductive history in combined pathology group 2 compared to infertility group 1 showed higher number of pregnancies (4.0 [3.0; 4.0] vs. 1.0 [0.0; 1.0]; p < 0.001), proportion of spontaneous miscarriages (50.9 % vs. 5.6 %; p < 0.001), prevalence of secondary infertility (24.5 % vs. 11.1 %; p < 0,001) and in vitro fertilization attempts (1.0 [0.0; 3.0] vs. 0.0 [0.0; 2.0]; p = 0.002). We found the difference in IL-1β gene expression in group 1 and group 3 (4.6 [3.5; 5.3]) vs. 4.9 [4.1; 5.8]; p = 0,044). This may suggest different mechanisms underlying endometrial-embryonic dialogue disorders with common inflammatory background: the general index of local inflammation was high in all groups (more than 60 %).
Conclusion. Prevalence of ultrasound chronic endometritis signs in groups 1, 2, 3 was up to 20 %. Patients with infertility and/or recurrent pregnancy loss, with chronic endometritis, concomitant dysbiotic disorders and activated local immunity need to correct vaginal microbiocenosis before pregnancy in order to prevent infectious and inflammatory complications. It is necessary to develop a screening program based on the characteristics of gynecological, obstetric, reproductive history, morbidity and local inflammatory gene expression levels. Our data confirm the importance of an integrated approach in assessing a role of infectious factor in origin of reproductive disorders.
What is already known about this subject?
► Vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) after antitumor therapy is associated with profound hypoestrogenism often coupled to severe clinical course.
► The role of local inflammation in VVA is well described, but systemic immuno-inflammatory markers have been poorly studied.
► Decreased estrogen levels are associated with altered regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and innate immunity components.
What are the new findings?
► For the first time, serum C3 and C4 levels were comparatively assessed in postmenopausal women with VVA coupled to varying clinical history such as chemoradiotherapy, antiestrogenic therapy, surgical menopause, as well as in women without gynecological cancer and healthy control.
► C3 and C4 levels remained within reference ranges in all groups but demonstrated consistent intergroup differences.
► The most pronounced complement-related differences were observed in women after chemoradiotherapy.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Assessing systemic immuno-inflammatory profiles may contribute to a better understanding of VVA pathogenesis coupled to clinical history.
► The findings may inform development of research-oriented and clinical assessment algorithms for VVA women with varying clinical history.
► The findings justify a need for conducting further studies focusing on activated complement components and their clinical relevance in VVA.
Introduction. Vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) is characterized by severe hypoestrogenism, impaired microcirculation, chronic inflammation, and decreased mucosal regeneration. In women with a varying clinical history, including applied antitumor treatment, such changes may differ in severity level. Despite that the role for pro-inflammatory cytokines in VVA has been extensively investigated, systemic immuno-inflammatory changes, primarily resulting in complement activation remained understudied.
Aim: to assess blood serum levels of C3 and C4 complement component levels in postmenopausal women with VVA coupled to clinical history, including various types of antitumor therapy, as well as in women without oncology history and in control group of healthy women.
Materials and Methods. A cross-sectional comparative study included five groups of postmenopausal women (n = 215): VVA after radical surgery (n = 52); VVA after chemoradiotherapy (CRT) (n = 27); VVA during antiestrogen therapy (n = 48); VVA without oncology history (n = 53); control group – healthy postmenopausal women (n = 35). The blood serum C3 and C4 levels were quantitated by immunoturbidimetry. The statistical analysis included the Kruskal–Wallis criterion and pairwise intergroup comparisons using the Mann–Whitney criterion with the Bonferroni correction.
Results. In all studied groups C3 and C4 levels were within the reference range, however, they differed significantly between the groups depending on the clinical history. The most prominent intergroup differences were observed in patients after CRT, who had higher C3 (1.62 g/L) and C4 (0.32 g/L) levels compared with control group (1.12 g/L for C3; 0.19 g/L for C4). In antiestrogenic therapy group (group 3) and surgical treatment group (group 1), C3 (1.48 g/L and 1.35 g/L, respectively) and C4 (0.28 g/L and 0.25 g/L, respectively) levels held an intermediate place between CRT group and control group. In women with VVA without oncology history, C3 (1.28 g/L) and C4 (0.23 g/L) levels were comparable to those in control group.
Conclusion. The data obtained evidence about variability of the systemic immuno-inflammatory profile in VVA driven by patient clinical history. Within the framework of the study, changes in C3 and C4 levels reflected general intergroup differences, which, however, remained within the reference range. The results emphasize a need for further research aimed at studying activated complement system components and their clinical significance in VVA.
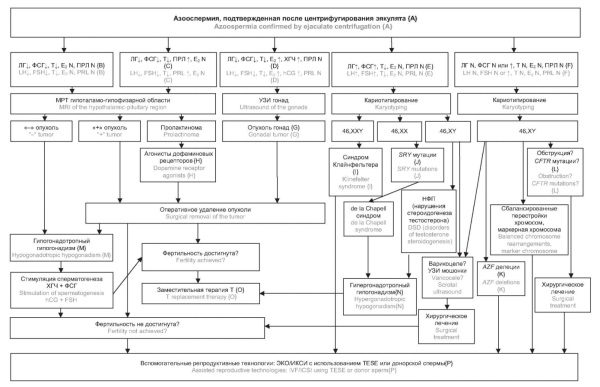
What is already known about this subject?
► Azoospermia occurs in approximately 1,0 % of men in the general population and in 10–15 % of infertile patients.
► Distinguishing between hypogonadotropic and hypergonadotropic forms of non-obstructive azoospermia determines both prognosis and treatment strategy.
► The standard diagnostic algorithm includes semen analysis, hormonal testing, ultrasound examination, genetic testing, and, if necessary, testicular biopsy.
What are the new findings?
► The forms of hypogonadism (hyper- and hypogonadotropic) and their contribution to developing azoospermia are examined in detail. Both original and international data on Klinefelter syndrome, microdeletions of the azoospermia factor (AZF) loci of the Y chromosome and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism are analyzed.
► An algorithm for the differential diagnosis between hypogonadotropic and hypergonadotropic azoospermia is presented.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Standardization of diagnostic algorithms will help reduce the number of diagnostic errors. The use of algorithms and markers for the differential diagnosis of azoospermia will enable successful application of pharmacological stimulation of spermatogenesis.
► Taking into account regional data will increase effectiveness of assisted reproductive technologies and support a personalized approach to patients with azoospermia.
Introduction. Azoospermia, defined as the absence of spermatozoa in the ejaculate after centrifugation, is one of the leading causes of male infertility, affecting approximately 1,0 % of men in the general population and up to 15,0 % of infertile patients. Timely differentiation between obstructive (ОА) and non-obstructive (NOA) azoospermia is critical for selecting appropriate treatment strategies, determining prognosis, and applying assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
Aim: to investigate the prevalence of different azoospermia forms of azoospermia in infertile men, within the context of real-world clinical practice at a non-specialized endocrine outpatient department, including personal observations, with consideration of/in comparison with the results of international and Russian epidemiological studies.
Materials and Methods. A comprehensive analysis of literature, clinical guidelines, and original data was performed. The study included 450 men aged 25–45 years with confirmed azoospermia. All patients underwent a comprehensive examination, including collection of anamnesis (reproductive, somatic, surgical); physical examination with assessment of secondary sexual characteristics, size and consistency of the testicles; double examination of ejaculate (centrifugation, microscopy); examination of blood hormone levels (follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, total testosterone, prolactin, anti-Müllerian hormone, sex hormone-binding globulin, inhibin B; if indicated – estradiol, thyroid-stimulating hormone, thyroxine); scrotum ultrasound examination with Doppler ultrasonography; genetic testing – karyotyping, testing for microdeletions of Y chromosome azoospermia factor (AZF) of the Y chromosome, CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) gene testing; when indicated, testicular sperm extraction (TESE) biopsy was performed.
Results. NOA and OA were identified in 63.3 % and 30 % of patients, respectively. Among NOA cases, the leading causes were idiopathic forms (19.6 %), Klinefelter syndrome (8.4 %), Y-chromosome microdeletions (5.8 %), and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (6.7 %). Varicocele was associated with NOA in 12 % of cases. These findings are consistent with global data, although minor ethnic and methodological differences were observed.
Conclusion. Azoospermia is a clinically and etiologically heterogeneous condition. Timely differentiation between its forms and the inclusion of genetic testing improve diagnostic accuracy and help optimizing management strategies. Standardization of diagnostic algorithms and a personalized approach increase ART effectiveness and the likelihood of fertility restoration.
What is already known about this subject?
► An infectious agent is a well-established cause of postpartum infectious and inflammatory diseases (IIDs). However, the current trend of increasing antibiotic resistance, the ability of pathogens to form "bacterial films," and the rapid metabolism of a considerable portion of antibiotic before it reaches an infection site markedly limit treatment effectiveness.
► A feature of endometritis after caesarean section (CS) is presented by atypical, erased course, a discrepancy between host response and severity of the inflammatory process, as well as developing complicated forms requiring repeated surgical intervention. A limited number of studies focusing on complicated endometritis forms after CS is available.
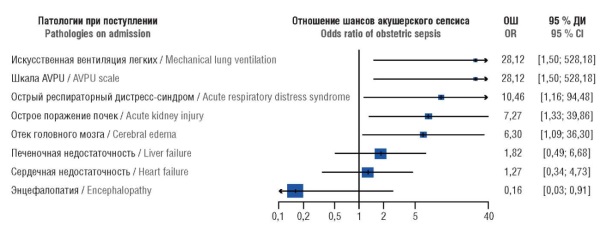
► Catastrophic obstetric conditions (COC) causing significant health damage and requiring large financial and medical resources represent a serious problem in obstetrics. After a COC, the risk of developing obstetric sepsis is extremely high in postpartum women, but the methods for its prediction remain poorly effective.
What are the new findings?
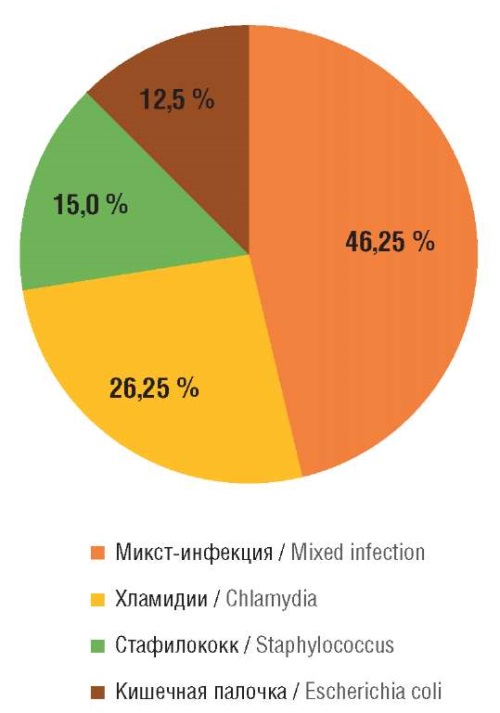
► Depending on the type of purulent-septic complications, S. epidermidis, E. coli, E. faecalis, E. faecium are shown to hold the leading role while analyzing causative microbial agents. Antibiotic resistance from 30.2 to 98.8 % was revealed in assessing the resistance of pathogenic microflora to antibacterial drugs.
► А method has been proposed for treating postpartum endometritis using the VNIITU-1PVP sorbent exerting antibacterial properties due to polyvinylpyrrolidone comprising at least 5.0 % content with high sorption capacity. Infrared spectrometry showed that the VNIITU-1PVP molded sorbent has a high sorption capacity for protein structures.
► A model for sepsis prediction has been developed with high sensitivity (94.5 %) and specificity (90.5 %).
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► A combined method for treating postpartum endometritis with the VNIITU-1PVP sorbent allows performing organ-preserving surgery (metroplasty) and lowering hysterectomy rate from 22.9 to 1.6 %.
► NEWS2 index is shown as the most informative tool for sepsis prediction in post-COC puerperant women.
Introduction. Infectious and inflammatory diseases (IIDs) represent a serious problem in modern obstetrics.
Aim: to improve methods for postpartum IIDs diagnosis, prognosis and treatment.
Materials and Methods. The study was conducted with 362 puerperants. At stage 1, there were retrospectively examined 199 patients with postpartum endometritis stratified as follows: IA (n = 113) – delivered by caesarean section (CS), IB (n = 86) – delivered by natural childbirth. At stage 2, a prospective, controlled study was conducted enrolling 163 puerperants. Group IIA (n = 124) consisted of patients with endometritis after CS, divided into 2 subgroups: subgroup IIA1 (n = 63) received antibacterial therapy and intrauterine sorbent VNIITU-1PVP, subgroup IIA2 (n = 61) – antibacterial treatment alone. Group IIB consisted of 39 puerperants who had a critical obstetric condition (COC), divided into 2 subgroups: IIB1 (n = 18) – patients with obstetric sepsis, IIB2 (n = 21) – without septic complications. Anamnestic data (complaints, disease history, characteristics of delivery, course of the postpartum period, timing of endometritis diagnosis), laboratory assay data (complete blood count, biochemical blood test, microbiological examination of uterine cultures, immunological study of IL-1β, IL-10, TNF-α cytokines in endometrial aspirate), and instrumental methods (ultrasound examination of pelvic organs, hysteroscopy, measurement of central venous pressure, infrared spectrometry of crushed carbon sorbent VNIITU-1PVP) were assessed. The APACHE, SOFA, NEWS2, AVPU scales were used to assess condition of post-COC puerperant women; χ2-test and Mann–Whitney test were applied to qualitative and quantitative variables to determine p-value. To develop a prognostic model for assessing obstetric sepsis in post-COC patients, the method of multiple logistic regression was used with step-by-step exclusion of variables until the minimum value of the Akaike criterion was reached. The obtained predictive formula was subjected to ROC analysis. Data calculations and graphical visualization were carried out using special libraries of the R language.
Results. In group IA vs. group IB patients, anemia (p = 0.004), leukocytosis (p < 0.001), a left shift in the leukocyte formula via leukocytosis (p < 0.001), hypoproteinemia (p< 0.001) were significantly more common, with Enterococcus faecalis (p = 0.02) and Enterococcus faecium (p = 0.02) more often cultured from the uterine cavity. The risk ratio of performing endometritis-related uterine extirpation in group IA was 5.33 (95 % CI = 1.43–19.78) compared with group IB. The use of the molded sorbent VNIITU-1PVP in subgroup IIA1 allowed 87.3 % to avoid microbial growth in the uterine cavity. The concentration of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in the uterine cavity in subgroup IIA1 was also significantly lower than that of in subgroup IIA2 – by 4.0 and 3.2 times, respectively (p < 0.05). In subgroup IIA1, organ-preserving surgery was performed in 23 cases related to failure of uterine sutures. While analyzing the data of group IIB patients, the following cut-off points were found: international normalized ratio – 1.13, central venous pressure – 6 mm Hg, aspartate aminotransferase level – 45 IU/L, and a mathematical model for post-COC sepsis development was constructed. The effectiveness of the developed prognostic model for obstetric sepsis in post-COC puerperant patients had 94.5 % sensitivity and 90.5 % specificity.
Conclusion. The use of the molded sorbent VNIITU-1PVP reduces a progression risk for uterine inflammatory process. Using a prognostic risk model for obstetric sepsis allows to timely identify this complication.
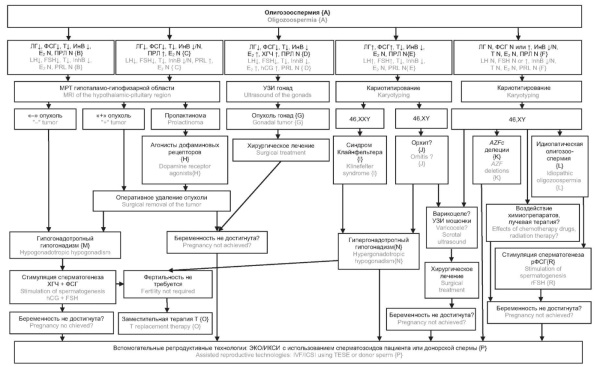
What is already known about this subject?
► Oligozoospermia is one of the leading causes of male infertility and is diagnosed in 15–20 % of patients seeking fertility evaluation.
► The most frequent etiological factors include endocrine disorders (hypogonadism), varicocele, and genetic abnormalities such as Klinefelter syndrome and Y-chromosome microdeletions.
► International and Russian clinical guidelines provide general diagnostic algorithms including semen analysis, hormonal profiling, imaging, and genetic testing.
What are the new findings?
► The examination data from 210 men aged 25–45 years with confirmed oligozoospermia and infertility helps to systematize the spectrum of the underlying causes in clinical practice.
► The pathophysiological mechanisms of hypogonadism, the clinical significance of AZF locus microdeletions, Klinefelter syndrome, and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism are examined in detail.
► Special attention is paid to hypogonadism and idiopathic oligozoospermia as the most common and potentially reversible causes of male infertility.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Application of a stepwise diagnostic algorithm will improve detection of reversible forms of oligozoospermia and guide timely treatment or referral for assisted reproductive technologies.
► Incorporation of genetic testing (karyotyping, Y-chromosome microdeletions) into the routine evaluation of men with severe oligozoospermia will enhance prognostic accuracy and enable personalized reproductive strategies.
► The findings may contribute to refinement of national clinical guidelines and everyday management of patients with male infertility.
Aim: to compare international and Russian epidemiological data on the causes of oligozoospermia and to develop differential diagnostics and patient management algorithm by taking into account endocrine, genetic and immunological factors.
Materials and Methods. A retrospective observational study included 210 men aged 25-45 years with confirmed oligozoospermia and infertility complaints. All patients underwent semen analysis according to the World Health Organization standards (2021), blood hormone testing (follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, total testosterone, prolactin, thyroid-stimulating hormone, estradiol, inhibin B, anti-Müllerian hormone, 17-hydroxyprogesterone), scrotal ultrasound, as well as genetic testing (karyotyping and Y-chromosome microdeletions). The data provided by international clinical guidelines, European Association of Urology (EAU, 2024), American Urological Association/American Society for Reproductive Medicine (AUA/ASRM, 2024), publications in Russian and English retrieved from PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus and eLibrary databases were analyzed.
Results. A wide spectrum of oligozoospermia causes was identified: endocrine disorders (hypo- and hypergonadotropic hypogonadism), Klinefelter syndrome, Y-chromosome microdeletions, varicocele, and obstructive forms. The pathophysiological mechanisms of hypogonadism, the clinical significance of Klinefelter syndrome, features of Y-chromosome azoospermia factor deletions, and the role of varicocele as a potentially reversible cause of male infertility are discussed in detail.
Conclusion. Differential diagnosis of oligozoospermia requires a comprehensive, stepwise approach. Incorporating repeated semen analysis, hormonal profiling, ultrasound, and genetic testing into the diagnostic algorithm enables identification of reversible causes (varicocele, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism) as well as timely diagnostics of genetic forms (Klinefelter syndrome, Y-chromosome microdeletions). This ensures a personalized therapeutic strategy and improves the effectiveness of assisted reproductive technologies.
What is already known about this subject?
► Currently, pelvic inflammatory diseases (PID) are known to be treated by using etiotropic and anti-inflammatory therapy.
► Local antibiotics use at the site of administration not only promotes direct drug action in the area of the affected organ but may also be associated with a lower risk of side effects due to reduced systemic exposure.
What are the new findings?
► Efficacy of video endoscopic technologies was assessed in PID treatment.
► A comparative analysis of the treatment results with and without video endoscopic technologies, and evaluation of long-term treatment outcomes were conducted.
► Normalization of clinical and laboratory indicators related to inflammatory response, normalization of menstrual-ovarian and reproductive functions in patients receiving parenteral therapy in combination with local antibiotic therapy was observed.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The data obtained suggest about feasibility of using video endoscopic technologies during combination treatment of PID patients who underwent diagnostic laparoscopy for differential diagnosis.
Aim: to access the efficacy and safety of antibacterial irrigation in the treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) using video endoscopic techniques.
Materials and Methods. A prospective comparative study was conducted. At the first stage, in the period from 2021 to 2023, 80 PID patients were treated, who underwent diagnostic laparoscopy to clarify the diagnosis. The patients were randomized into 2 groups: main group received parenteral antibacterial therapy in combination with local antibacterial therapy by delivering an antibiotic solution to the surgical site via microirrigator; comparison group received standard parenteral antibacterial therapy. During treatment, all patients were assessed for clinical and laboratory parameters of the inflammatory process: febrile period length and tachycardia recorded; severity of pain syndrome assessed using a visual analogue scale (VAS); level of C-reactive protein (CRP) measured; performed a clinical blood test with analyzing leukocyte formula; performed pelvic organs ultrasound examination. The second study stage was carried out in 2024–2025 by further outpatient monitoring of patients to assess long-term sequelae, as well as repeated exacerbations and pregnancy onset term consequences, as well as the presence of repeated exacerbations and the onset of pregnancy.
Results. On day 5 after diagnostic laparoscopy in main group, the CRP level and leukocytosis indicators normalized in 50,0 and 55,0 % patients, respectively; in comparison group, normalization of such indicators was observed in 27.5 % (p = 0.039) and 32.5 % (p = 0.043) cases, respectively. At discharge, white blood cell count and WBC differential were normal in 92.5 % and 75.0 % (p = 0.034) patients in main and comparison group, respectively. Febrile period length in main group was 2-fold shorter than in comparison group; duration of tachycardia remained unaffected. On day 5 after diagnostic laparoscopy, the level of pain syndrome in main group was smaller by 2-fold than in comparison group. At discharge, the patients from main group had a more favorable pelvic organs ultrasound picture showing a decreased number of patients in the former having increased ovarian volume to 12 ml, with hyperechoic areas, tubal thickening (p = 0.034), detected varying amounts of fluid in the pelvic area (p = 0.027), higher number of patients without pathology of the pelvic organs based on ultrasound data (p = 0.041). In patients who received combination treatment (main group), pregnancy occurred 2 times more often than in those treated solely with standard drug therapy (comparison group). In addition, normalized menstrual cycle was noted significantly more often (p = 0.007) in main group – 17 (42.5 %) vs. 6 (15.0 %) cases in comparison group. While assessing the development of complications and repeated exacerbations, no statistically significant inter-group differences were found.
Conclusion. The method we propose can be considered as an alternative treatment option for PID patients, who were referred to undergo diagnostic laparoscopy during differential diagnostics. Taking into consideration the lack of highquality randomized studies that would definitively confirm our results, it seems relevant to continue further investigation on this issue.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about this subject?
► Obstetric bleeding is one of the leading causes of maternal mortality.
► The main etiologies include uterine atony, birth canal lacerations, and thrombocytopathies.
► Prompt medical intervention is crucial to prevent complications.
What are the new findings?
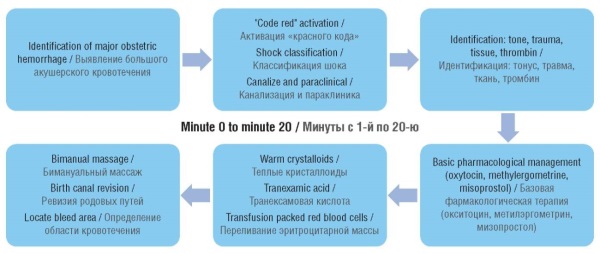
► The authors provide a treatment algorithm based on the recommended time frame for managing postpartum hemorrhage.
► Hemostatic agents must integrate a multimodal approach to treat postpartum hemorrhage.
► Tranexamic acid is mandatory in all postpartum hemorrhages because it reduces mortality by 33 %.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The implementation of multimodal approaches may reduce postpartum hemorrhage mortality.
► Functional hemodynamic monitoring, appropriate use of blood products, and resource management could positively affect maternal-fetal prognosis.
► The point-of-care diagnostic tests can optimize clinical management and save resources.
Obstetric bleeding represents one of the main causes of maternal mortality worldwide. Along with hypertensive disorders it accounts for over half of maternal mortality cases. The implementation of strategies such as the "code red", increased institutionalized deliveries, early transfusions, and early obstetric alert system has reduced mortality. Cases of massive bleeding require admission to the Intensive Care Unit as they can progress to coagulopathy. This narrative review focuses on medications intended for the advanced management of coagulopathy in this population.
What is already known about this subject?
► Nectin-4 is a cell adhesion molecule belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, involved in the formation of intercellular junctions and cell migration. It has been extensively studied as a tumor-associated biomarker in various epithelial malignancies.
► Nectin-4 expression is elevated in several solid tumors, including breast, lung, and bladder cancers. It is implicated in promoting angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to anticancer therapies.
► In gynecologic oncology, nectin-4 is regarded as a promising diagnostic and therapeutic target, particularly in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma and cervical cancer; however, its role in rare tumors and benign conditions remains poorly understood and under investigated.
What are the new findings?
► An association between nectin-4 expression and mismatch repair deficiency in endometrial cancer has been established, which correlates with shorter progression-free survival. This supports nectin-4 prognostic significance in tumor molecular stratification.
► High sensitivity and specificity of both serum and tissue nectin-4 levels have been demonstrated in serous ovarian cancer, particularly in patients with normal CA-125 range. This justifies nectin-4 use as an independent biomarker for early diagnostics.
► The experimental efficacy of nectin-4 inhibitors (NQC, 9MW2821, ADRX-0706) has been shown in cervical and ovarian cancers, including chemoresistant counterparts, confirming its potential as a therapeutic target for personalized medicine.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Nectin-4 could be integrated into diagnostic panels for early detection of ovarian cancer, particularly in patients with normal CA-125 levels, thereby improving screening sensitivity and reducing percentage of advanced-stage cases.
► Given a prognostic value in mismatch repair-deficient tumors, nectin-4 expression may guide therapeutic decision-making and help identify candidates for intensified treatment or enrollment in clinical trials.
► The development of nectin-4–targeted agents opens up an avenue for personalized therapy in cervical and ovarian cancers, including chemoresistant cases, potentially enhancing treatment efficacy while minimizing systemic toxicity
Introduction. Nectin-4, a cell adhesion molecule of the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF), has been extensively studied in oncological diseases. Nectin-4 is involved in the formation of intercellular connections and promotes tumor cell proliferation, migration and chemoresistance. Upregulated nectin-4 expression has been detected in various malignant neoplasms, including tumors of the female reproductive system – ovarian, endometrial, cervical cancer, as well as rare tumors of the vulva, vagina and fallopian tubes.
Aim: to summarize current data on nectin-4 role in the pathogenesis, diagnostics, prognosis and therapy of malignant tumors of the female reproductive system, and to assess the prospects for its clinical use in personalized medicine.
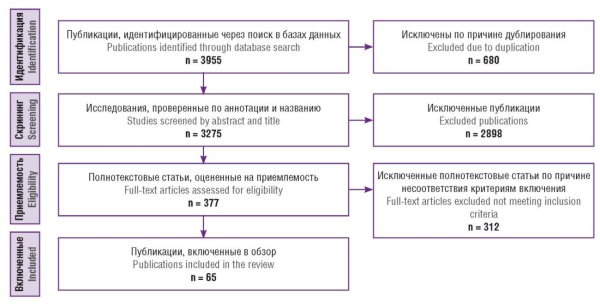
Materials and Methods. A search for relevant publications was conducted in the PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase and eLibrary.ru databases beginning from January 2000 to December 2024. The inclusion criteria covered original and review articles devoted to nectin-4 in gynecological oncology. Key words in Russian and English, Boolean operators, and filtering by full-text, subject matter, and quality of research were used. From the 3955 identified publications, 65 were included in the review.
Results. Nectin-4 expression is associated with enhanced tumor cell proliferation, migration, and chemoresistance, whereas its involvement in generating tight intercellular junctions promotes the development of chemoresistant spheroids. In ovarian cancer, upregulated levels of nectin-4 messenger RNA (mRNA) and serum protein demonstrated high diagnostic and prognostic significance, especially in combination with traditional markers such as cancer antigen 125 (CA-125). In endometrial cancer, nectin-4 expression correlates with a deficiency of the mismatch repair system (MMR genes) MSH2/MSH6 genes and lowered progression-free survival. In cervical carcinoma, nectin-4 is related to drug resistance, thereby positioning it as a promising target for novel treatment strategies. The latter using nanoquinacrine and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) such as 9MW2821 and ADRX-0706, are currently undergoing clinical trials. Additionally, nectin-4 has shown relevance in non-malignant reproductive disorders such as endometriosis and preeclampsia.
Conclusion. Nectin-4 demonstrates high clinical significance as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in gynecological malignancies. Its expression is associated with aggressive disease progression and drug resistance, especially in ovarian, endometrial and cervical cancers. Clinical trials with nectin-4-targeted drugs, including ADCs, are underway. Thus, nectin-4 represents a promising target for the development of personalized diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in gynecological oncology.
What is already known about this subject?
► Extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a key role in intercellular communication and are involved in the regulation of tumor growth and metastasis.
► EVs carry biologically active molecules, including microRNAs and proteins that influence angiogenesis, proliferation, and chemoresistance.
► Current research highlights EVs potential as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in gynecologic cancers, including cervical, endometrial and ovarian cancers.
What are the new findings?
► Exosomal microRNAs-21 – miR-200b, and miR-200c are associated with low survival in malignancies of the female reproductive system.
► The LGALS3BP protein in exosomes is associated with angiogenesis and progression of endometrial cancer; its high levels correlate with metastases and worse outcomes.
► MicroRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in exosomes are associated with the progression, metastasis, and response to gynecological tumor therapy.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► The introduction of exosomal biomarkers will improve early diagnosis and monitoring of gynecological tumor recurrence.
► The use of exosomal profiles will ensure more accurate patient stratification and individualization of treatment regimens.
► Non-invasive methods based on exosome analysis will increase screening availability and reduce a need for invasive procedures.
Malignant neoplasms of the female reproductive system remain a significant global health concern, ranking among the leading causes of cancer incidence and mortality in women. Despite advances in the field of gynecologic oncology, early diagnosis and prognosis of such diseases continue to pose substantial challenges. In recent years, extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes, microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies, have been increasingly attracted attention as key mediators of intercellular communication and carriers of biologically active molecules. EVs transport microRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, proteins, and other molecules that influence critical carcinogenic processes such as proliferation, angiogenesis, metastasis, and the development of chemoresistance. This review summarizes current data on the EVs role in the pathogenesis and progression of cervical, endometrial, and ovarian cancers. The diagnostic and prognostic potential of EV-associated biomolecular components is examined, with evidence from preclinical and clinical studies highlighting their promise as biomarkers. The review also discusses the prospects for clinical application of EVs, emphasizing the challenges of methodological standardization and the need for multicenter studies to validate their clinical utility. Additionally, the importance of integrating omics technologies and bioinformatics approaches is underscored as essential for improving patient stratification and advancing personalized therapy.
What is already known about this subject?
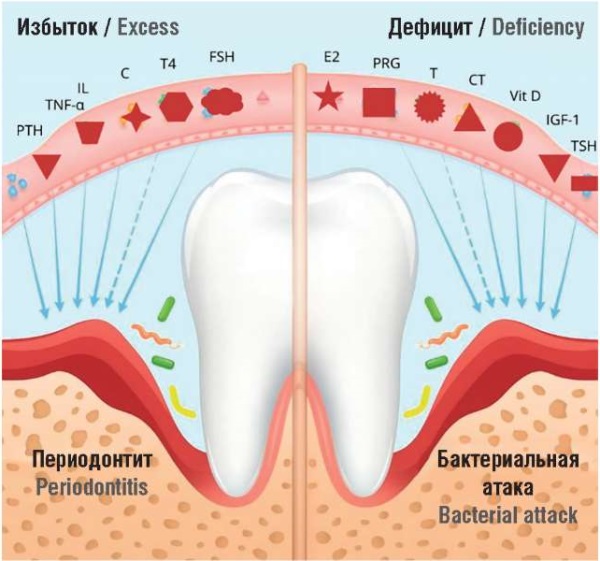
► Postmenopausal osteoporosis is associated with an increased risk of dental implant failure. Hypoestrogenism, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) deficiency impair alveolar bone microarchitecture. Antiresorptive therapy with bisphosphonates and denosumab increases bone density but is associated with the risk of jaw osteonecrosis.
What are the new findings?
► The effects of bioidentical forms of estradiol and progesterone on dental implant osseointegration are discussed.
► Data on the role of calcitonin, follicle-stimulating hormone, and systemic inflammation in predicting implant outcomes are presented.
► A concept of combined use of bioidentical estrogens and progestogens as a part of menopausal hormone therapy in postmenopausal women planning dental implantation is proposed.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► It may allow for individualized planning of implant preparation in postmenopausal women; justify the rationale for preliminary hormonal correction in women planning dental implantation; expands interdisciplinary collaboration between dentists, endocrinologists, and gynecologists.
Here, we summarize current evidence on the impact of postmenopausal osteoporosis, menopause-related hormonal changes, and hormone therapy on dental implant outcomes. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of bone alterations are reviewed, with particular emphasis on the role of estrogen, progesterone, calcitonin, growth hormone, and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) deficiency. Special attention is paid to the effects of menopausal hormone therapy and bioidentical forms of estradiol and progesterone on osteoporosis course and the effectiveness of dental implantation. The analysis highlights the risks of implant loss and the opportunities of interdisciplinary approach in dentistry and endocrinology to optimize implant osseointegration in postmenopausal women.
CLINICAL CASE
What is already known about this subject?
► Ovarian tumors in children and adolescents represent common and high-priority issue.
► This disease can be long asymptomatic, manifesting only with development of complications.
► The most common differential diagnosis of ovarian cysts in adolescents is performed with acute appendicitis, appendicular infiltrate and ectopic pregnancy.
What are the new findings?
► Ovarian cysts in adolescents can be complicated by hydronephrosis.
► The pathogenesis of this complication is based on obstruction of the urinary tract due to compression by large-size ovarian cyst.
► In case of benign ovarian tumors and the presence of viable ovarian tissue, cystectomy is the surgery of choice.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
► Reducing the amount of surgery to cystectomy allows for minimal damage to the adolescent's reproductive potential in the future.
► Adnexectomy is advisable only in the case of a cyst complication such as ovarian torsion leading to ovary necrosis.
Introduction. According to the average statistical data, the incidence of ovarian tumors in children comprises about 4.6 %. In the adolescent population, ovarian epithelial tumors confidently hold a leading place. One of their histological subtypes is presented by mucinous cystadenoma. Due to the frequent asymptomatic course or the absence of specific clinical features, such cysts can long persist in the abdominal cavity and reach significant sizes. In the latter case they can manifest with the symptoms of serious complications such as obstruction of the urinary tract and the intestines, pedunculated masses torsion, ovarian torsion, rupture of cysts, etc. Thus, the main insidiousness of ovarian tumors lies in the delayed diagnostics and omitted surgical opportunities for ovary preservation.
Aim: to present a clinical case of a teenage girl with giant ovarian cystadenoma complicated by hydronephrosis due to ureteral compression.
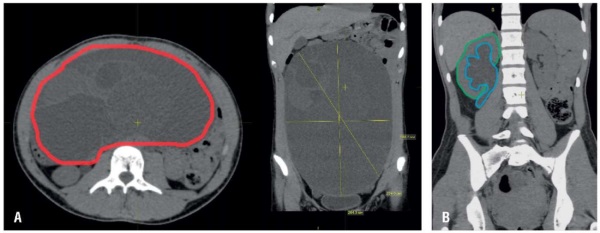
Case presentation. A female patient R., 17 years old, was admitted to the surgical department on 12.02.2025, with complaints of abdominal enlargement, abdominal pain lasting over 4 months, frequent urinal miction and algodismenorrhea. Medical history dated of January 2025 showed that imaging research methods performed in different organizations revealed a multilocular cyst of the abdominal cavity – a mucinous cystadenoma of the left ovary, sized 193×195×271 mm, complicated by hydronephrosis of the right kidney. Physical examination revealed a local abdominal pain in the umbilical region as well as increased abdominal volume. General blood test found signs of mild iron deficiency. Blood screening tests for serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and cancer antigen-125 (CA-125) levels allowed to exclude oncological pathology.
Results. Further surgical treatment was performed. On 17.02.2025, patient R. underwent laparoscopic cystectomy. The passage of urine quickly returned to normal after removal of obstruction cause. A follow-up ultrasound examination on the day 7 post-surgery showed that the pelvis of the right kidney was markedly decreased. The postoperative period was unremarkable. Patient R. was discharged on day 8 with improvement. Recommendations were provided.
Conclusion. A clinical case presented here demonstrates an opportunity for developing complication such as hydronephrosis related to bulky ovarian cyst in adolescents. The surgical treatment confirms that even in case of giant cysts, cystectomy along with preserving maximum volume of the ovarian tissue may be performed thereby allowing to exert reproductive function in the future. However, such surgical treatment option should be performed only with confidence in benign tumor origin and presence of viable ovarian tissue.
FROM HISTORY
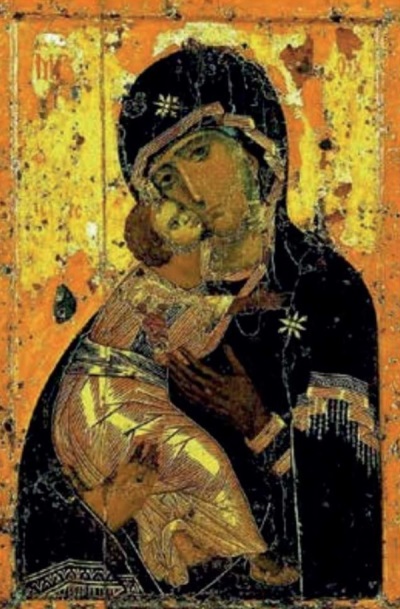
The article explores the image of the Virgin and Child as a central theme in Byzantine and Russian iconography. Timeless and universal significance of this theme in art is emphasized primarily focusing on a detailed analysis of four key miraculous icons of the Mother of God: the Vladimir, Iveron, Donskoy, and Kazan icons. Historical origins, iconographic features, and role in the fate of Russia are examined for each icon. The article traces the profound spiritual connection between such images and national history, highlighting the moments when their intercession, according to believers, saved the country from enemy invasions and internal crises – from Tamerlane's invasion and liberation from the Mongol-Tatar yoke to the Time of Troubles, the Patriotic War of 1812, and the Great Patriotic War. The interaction between state and church is illustrated by examples of the icons transfer for public prayer and symbolic gestures of the Soviet government during the Great Patriotic War. The image of the Mother of God is an enduring symbol of maternal love, hope, and spiritual unity.
EVENTS

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2500-3194 (Online)